Figure 5.
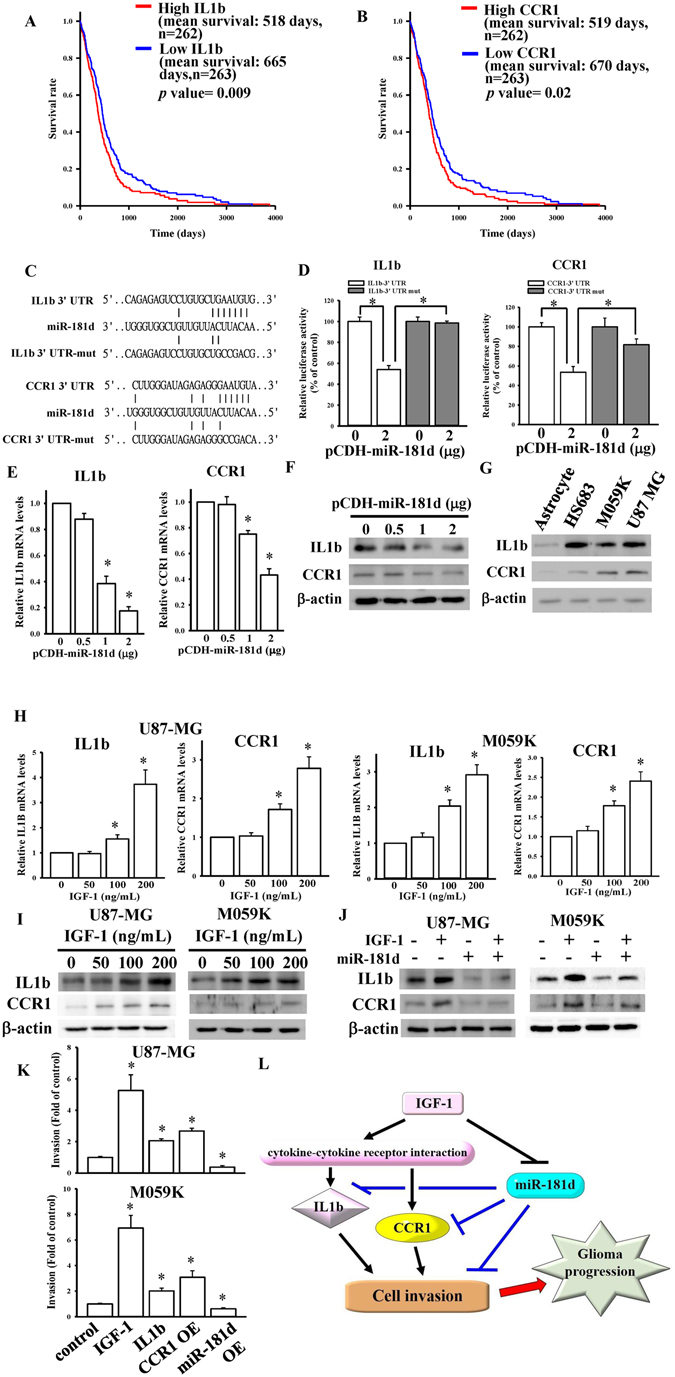
Interleukin (IL)-1b and C-C chemokine receptor type 1 (CCR1) were identified as direct target genes of miR-181d. Kaplan-Meier survival curves were analyzed in the IL-1b (A) and CCR1 (B) groups. The survival rate was calculated by multivariate permutation tests (with a false discovery rate (FDR) of <0.01). TCGA GBM patients were divided into two groups based on the median expression cutoff points of IL-1b and CCR1 levels. (C) Schematic diagram of potential miR-181d-targeted sites in the 3′-untranslated region (UTR) of the IL-1b and CCR1 genes. (D) Effects of miR-181d on 3′UTR luciferase activity of the IL-1b and CCR1 genes. To test for miR-181d’s effect, different doses of miR-181d-expressing plasmids were co-transfected with 500 ng of the pmiRGlo-3′UTR or mutant 3′UTR of the IL-1b and CCR1 genes. Luciferase activity was measured in these cells 24 h after transfection. Effects of miR-181d overexpression on mRNA (E) and protein (F) expressions of the IL-1b and CCR1 genes. (G) Detection of endogenous protein levels of the IL-1b and CCR1 genes in normal human astrocytes and three different glioma cell lines including HS683, M059K, and U87-MG cells. Dose-dependent effects of IGF-1 on mRNA (H) and protein (I) expressions of the IL-1b and CCR1 genes. Data are the mean ± SD of three experiments. *p < 0.05. (J) The effects of miR-181d on IGF-1-mediated IL-1b and CCR1 protein levels. (K) The effects of IGF1-miR181d-cytokines axis on glioma cell invasion. After cells were respectively treated with 100 ng/ml IGF-1, 10ng/ml IL1b, or transfecting with CCR1 and miR-181d overexpressing plasmids, the cell invasion changes were measured by matrigel invasion assays. Data are the mean ± SD of three different fields. *p < 0.05 compared with control. (L) Schematic diagram shows IGF-1 expressions are highly associated with cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, especially in regulations of IL1b and CCR1, both are miR-181d direct target genes. IGF-1 enhances IL1b and CCR1 expressions via reducing miR-181d levels, resulting in glioma cell invasion and progression.
