Figure 5.
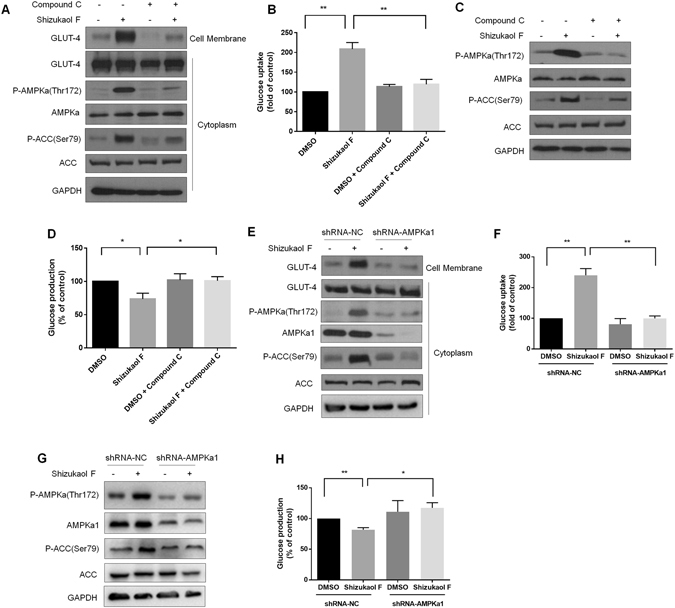
Shizukaol F regulates glucose metabolism via AMPKa phosphorylation activity. C2C12 myotubes were pretreated with 20 μM AMPK inhibitor compound C, and followed by the treatment of 1 μM shizukaol F. Then the immunoblotting analysis of AMPKa phosphorylation and GLUT-4 translocation were measured (A); and the determination of glucose uptake (B). **P < 0.01 (two-tailed Student t-test). n = 6 independent biological replicate experiments. Primary hepatocytes were pretreated with 10 μM compound C, and followed by the incubation of 1 μM shizukaol F. Then the western blotting (C) and gluconeogenesis level were detected (D). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 (two-tailed Student t-test). n = 6 independent biological replicate experiments. C2C12 cells infected by lenti-virus of shRNA-AMPKa1 were treated with 1 μM shizukaol F for 24 h. AMPKa phosphorylation and GLUT-4 translocation were analyzed by western blotting (E). Glucose uptake was measured (F). **P < 0.01 (two-tailed Student t-test). n = 3 independent biological replicate experiments. Primary hepatocytes were transfected with shRNA-AMPKa1 lenti-virus or a negative control. Cells were incubation with 1 μM of shizukaol F for 24 h. AMPKa and ACC phosphorylation were analyzed (G), and gluconeogenesis level was measured (H). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 (two-tailed Student t-test). n = 3 independent biological replicate experiments.
