Figure 6.
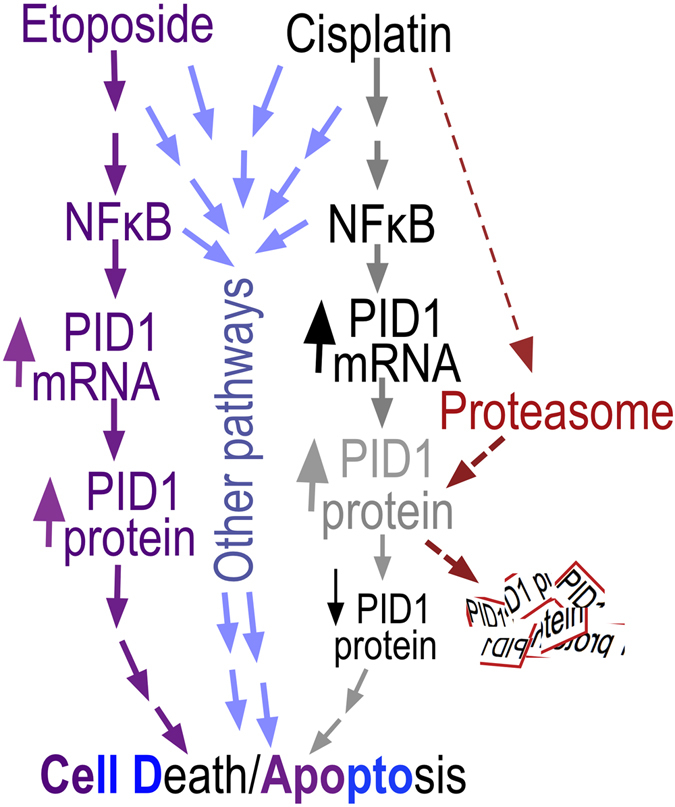
PID1 in chemotherapy-induced medulloblastoma and glioma apoptosis. The data suggest that PID1 contributes to chemotherapy-induced apoptosis through an NFκB-dependent mechanism as follows: Etoposide and cisplatin both increase PID1 mRNA via NFκB and both increase apoptosis. While etoposide increases both PID1 mRNA and PID1 protein, cisplatin increased PID1 mRNA, but decreased PID1 protein. The cisplatin-induced decrease in PID1 protein is reversed by bortezomib, suggesting that it is due to proteasomal degradation. It is likely that both etoposide and cisplatin activate additional signaling pathways that contribute to apoptosis.
