Figure 3.
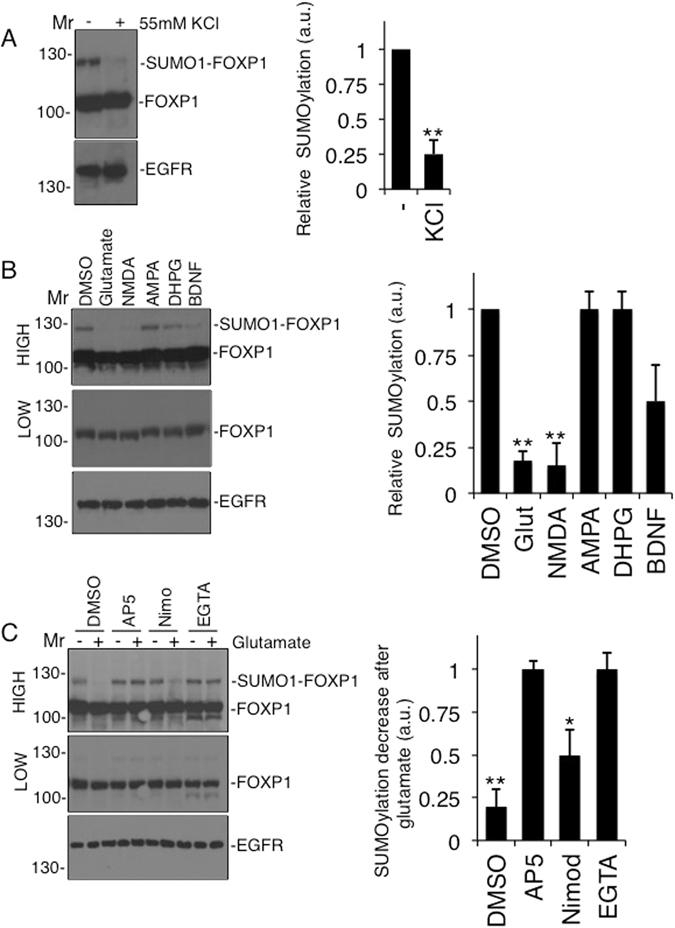
Activity-dependent regulation of FOXP1 SUMOylation. (A) Cultured cortical neurons (DIV7) were depolarised for 30 min with KCl in ACSF, lysed in sample buffer and resolved by SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Student’s t-test, n = 4, **p < 0.01. (B) Cortical neurons were treated with the indicated drugs, lysed in sample buffer and samples resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting. NMDA receptor activation decreases FOXP1 SUMOylation. Note the lower exposure in the middle panel indicates unchanged expression levels of unmodified FOXP1. Student’s t-test and Welch correction, n = 5 **p < 0.001. (C) Calcium entry through NMDARs and L-type calcium channels reduces FOXP1 SUMOylation. Cultures were pre-treated with the NMDAR antagonist AP5, the L-type calcium channel blocker nimodipine or EGTA to chelate extracellular Ca2+ prior to glutamate stimulation. Data normalised to no glutamate, DMSO control. ANOVA, n = 5, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05.
