Figure 5.
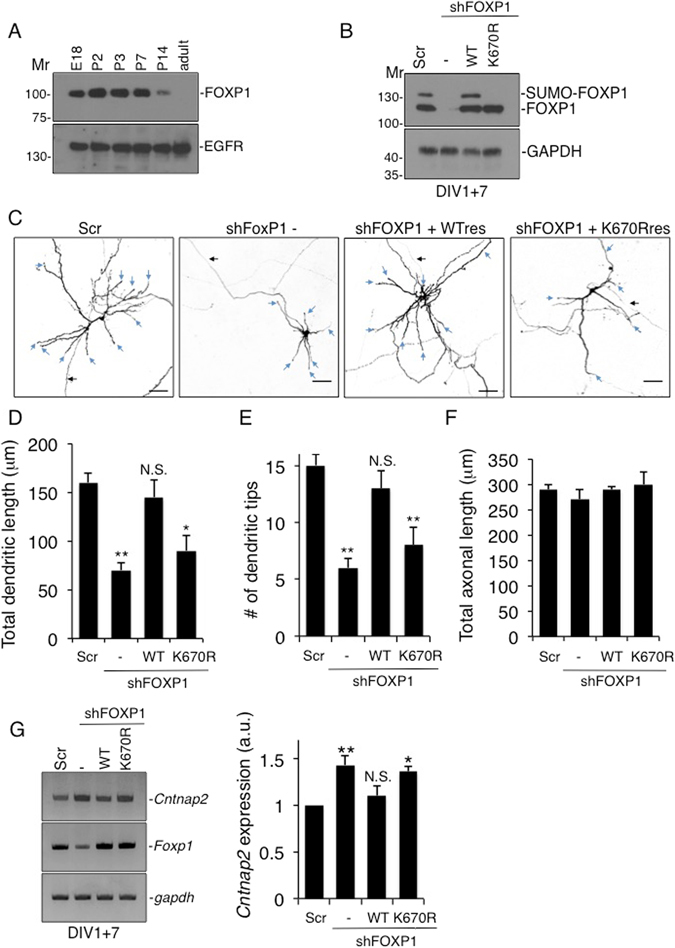
SUMOylation of FOXP1 regulates dendritic outgrowth and length. (A) Expression of FOXP1 peaks during early development. Non-denaturing lysates of either embryonic or postnatal brain cortices were analysed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting. (B) Cortical neurons lentivirally-infected with the indicated knockdown or knockdown plus FOXP1-WT or FOXP1-K670R rescue constructs at DIV1 were cultured for a further 7 days and then lysed in sample buffer and resolved by immunoblotting. (C) SUMOylation of FOXP1 is required for dendritc outgrowth. DIV1 cultured cortical neurons were transfected with constructs expressing either scrambled shRNA, FOXP1 shRNA or FOXP1 shRNA plus FOXP1-WT or FOXP1-K670R rescue and prepared for imaging at DIV8. In all images of neuronal morphology, blue arrows and black arrowheads indicate dendrites and axons, respectively. Scale bar, 10 μm. (D) Knockdown of FOXP1 significantly shortens dendritic length. FOXP1-WT but not the SUMOylation-deficient FOXP1-K670R rescued the dendritic phenotype. 312 neurons were analysed using the neuron J plugin for Image J. ANOVA, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05. (E) Knockdown of FOXP1 significantly reduces the total number of dendritic tips. FOXP1-WT but not the SUMOylation-deficient FOXP1-K670R rescued the deficit in dendritic tip number. 302 neurons were analysed using the neuron J plugin for image J. ANOVA, **p < 0.01. (F) Axonal length was not significantly different between any FOXP1 knockdown or rescue with either WT-FOXP1 or the SUMOylation-deficient K670R FOXP1 mutant. (G) Knockdown of FOXP1 significantly increases Cntnap2 expression. DIV1 cultures were infected as in C, followed by RNA extraction and RT-PCR analysis. FOXP1-WT but not the SUMOylation-deficient FOXP1-K670R rescued Cntnap2 transcript levels back to control levels. ANOVA, n = 4, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05.
