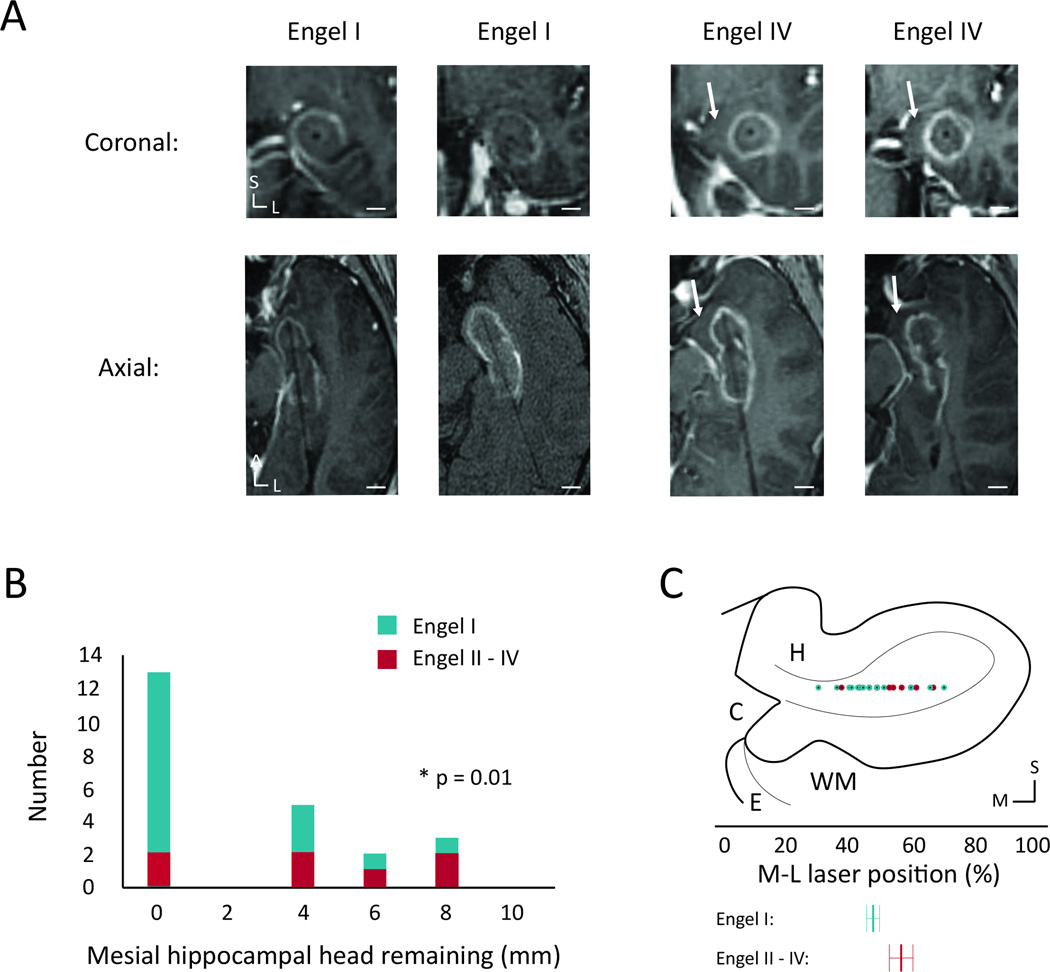
Figure 2. Ablation of mesial hippocampal head and seizure freedom.
(A) Coronal and axial intraoperative contrasted fast-spin gradient echo images of the laser trajectory through the ablated hippocampal head for two sample Engel I patients and the two Engel IV patients, showing a lateral trajectory with sparing of medial hippocampal tissue for the Engel IV patients. (B) Histogram showing the distribution of thickness of remaining unablated hippocampal head tissue medial to the ablation zone calculated from the same image sequences. (C) Coronal diagram of the hippocampal head showing the M-L distribution of the laser positions, determined from the posterior-most section through the hippocampal head. Below are shown averages for the two Engel groups with std. error shown using the error bars. White scale bars: 0.5 cm. C – cistern, E – entorhinal cortex, H – hippocampus, WM – white matter tracts; L – lateral, M – medial, S – superior.