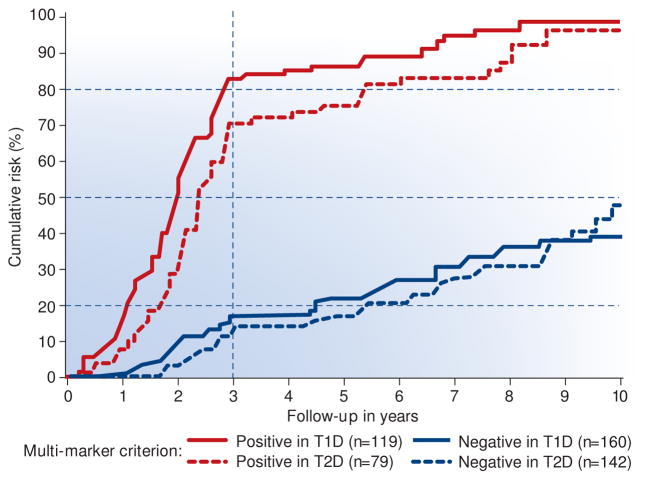
Figure 5.
Cumulative risk of ESRD during 10 year follow-up in the two Joslin cohorts with chronic kidney disease according to value of multi-marker criterion at entry into the follow-up.
The following markers at baseline were considered: ACR, eGFR, TNFR1 and TNFR2 to develop the multi-marker criterion to identify patients (fast decliners) at risk of ESRD during the first 3 year of follow-up using data from T1D cohort. The performance of the criterion was replicated in the data from T2D cohort.
Positive criterion: at baseline serum TNFR1 >4.3 ng/ml disregarding the other markers, or serum TNFR1 between 2.9 and 4.3 ng/ml and ACR >1.9 g albumin/g creatinine in urine.
Negative criterion: at baseline serum TNFR1 <4.3 ng/ml and ACR <1.9 g/albumin/1 g creatinine in urine, or serum TNFR1 <2.9 ng/ml disregarding values of other markers.
It was extraordinary that the multi-marker criterion that was developed in the T1D cohort produced almost identical stratification according to ESRD risk in T2D cohort. The T2D cohort had very different clinical characteristics than the T1D cohort.
Re-analyzed data from Yamanouchi M et al. Kidney Int 2016 (under review).44