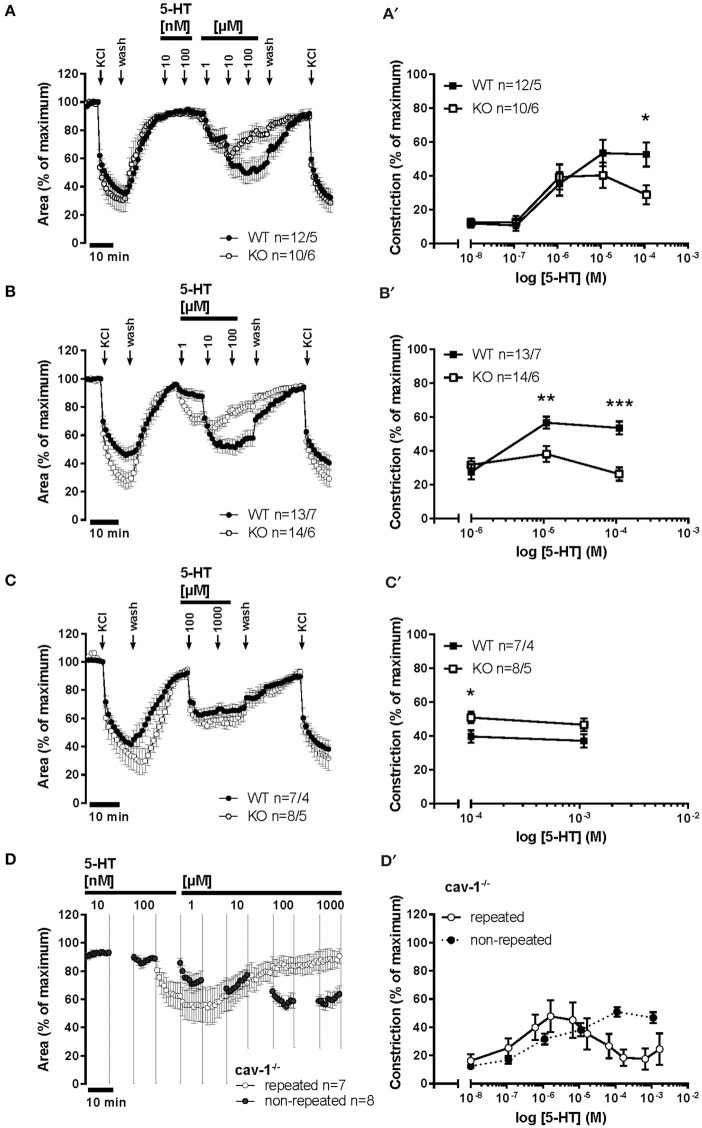
Figure 7.
5-HT-mediated changes in the luminal area of peripheral bronchi from cav-1+/+ and cav-1 −/− mice. Videomorphometric analyses of PCLS. (A,A') Bronchi of cav-1+/+ and cav-1−/− mice responded to increasing 5-HT doses. 5-HT-induced constriction in cav-1−/− mice PCLS was significantly reduced at μM concentrations of 5-HT compared to cav-1+/+ mice strain. We applied KCl (60 mM) as a viability control for 5 min at 2 points of experiment. (B,B') Bronchi of cav-1+/+ and cav-1−/− mice responded to increasing 5-HT doses. 5-HT-induced bronchoconstriction in PCLS was significantly reduced at μM concentrations in cav-1−/− mice compared to cav-1+/+ mice. (C,C') Bronchi of cav-1+/+ and cav-1−/− mice responded to 5-HT with a rapid sustained constriction. (D,D') Comparison of the response to 5-HT after repetitive stimulation (in half logarithmic mode) with the direct (non-repetitive) 5-HT response. The intrapulmonary bronchi of cav-1−/− mice exhibit a decrease in 5-HT-induced bronchoconstriction after repetitive 5-HT application. Data are presented as mean of number of bronchi (n)/number of animals ± SEM. *p ≤ 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001, Student's unpaired t-test with the exception of values at 1 mM 5-HT in (C') which was analyzed by Mann-Whitney U-test.