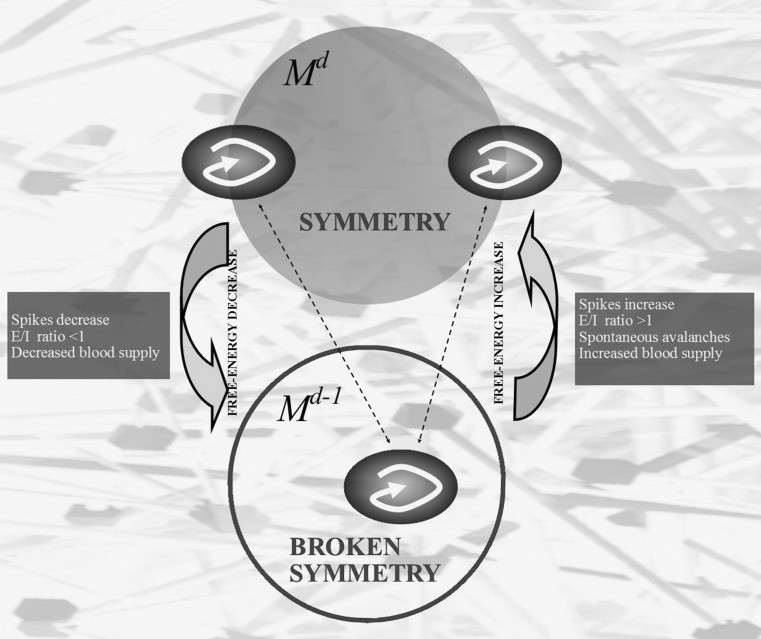
Fig. 1.
The manifold M d displays two antipodal points with matching description. It this case, according to BUT variants’ dictates, the antipodal points stand for two symmetric functions equipped with the same energetic conformation (black ovals containing curved arrows). When a symmetry break occurs, the manifold M d−1 displays just a single function, equipped with an energetic level lower than the sum of the antipodal functions’ ones. Therefore, dimension loss occurs together with a decrease of energy. The lateral dark boxes illustrate some hypothetical but plausible conditions which might cause increase or decrease of energy in the brain. In sum, the system displays a configuration with higher energy in M d, and with lower energy when a symmetry break occurs. The background stands for a schematized structure of the brain phase space