Figure 2.
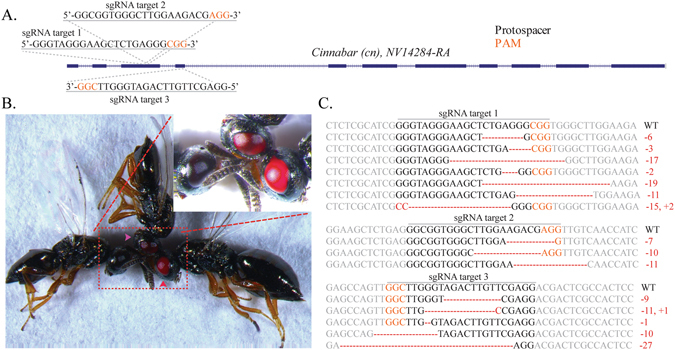
CRISPR/Cas9 target sites, mutant cinnabar phenotypes, and sequence disruption confirmations. Three independent sgRNAs were designed to target cinnabar in either exon 3 (sgRNA target 1 & 2) or exon 4 (sgRNA target 3) as depicted (A). Following embryo microinjection, surviving cinnabar mutant G0 adult wasps were readily observable with a light microscope by simply observing eye color phenotypes. Black eyes are wild-types, while bright red (younger - within a few days of emergence; indicated by red arrowhead) and red (older - roughly a week postemergence; indicated by purple arrowhead) are mutants with different age (B). Many mutants for each sgRNA were established and deletions and insertions were readily detected via sequencing. The black cn+ pigmentation appears normally during pupal development. However, in CRISPR-induced cn mutants, the garnet-colored eye never undertakes a black phenotype and can be easily seen in adults. These mutant phenotypes can also be scored in late pupal stages (not shown) (C). PAM sequences (NGG) are indicated in orange, and cn gene disruptions resulting from insertions/deletions are indicated in red.
