Figure 2.
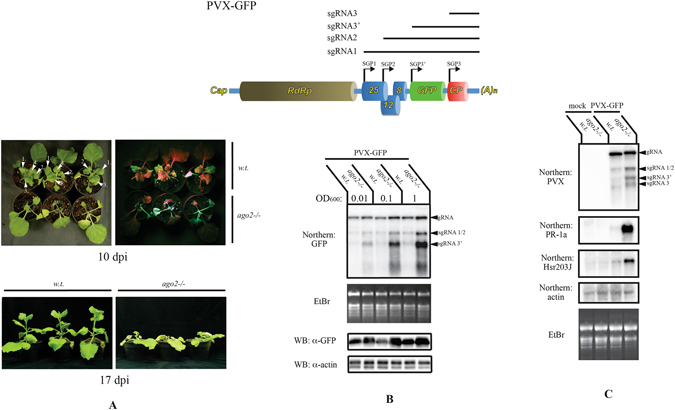
ago2 mutant N. benthamiana plants are hyper-susceptible to PVX infection. (A) Photographs of PVX-GFP infected plants. As a sign of recovery new leaves were starting to emerge in wild-type plants, which were generally absent in ago2 plants. On the top left panel white arrowheads point to newly emerging leaves, with higher numbers indicating younger leaves. Picture of the same plants was taken under UV light (top right panel). In the wild-type plants the new leaves exhibited gradually reduced GFP signals with decreasing age. At 17 dpi, wild-type plants show recovery, while in the ago2 plants the apical necrosis usually results in plant death (bottom panel). (B) PVX infections of wild-type and ago2 N. benthamiana plants were initiated from a leaf-infiltrated Agrobacterium strain carrying a PVX-GFP encoding binary vector. Different dilutions of the bacterium suspension were infiltrated into the leaves. Concentrations of the suspensions are given as optical densities measured at 600 nm (OD600). At 5 dpi, total RNA and protein lysates were prepared from the first symptomatic non-inoculated leaves. Samples were collected from three plants and pooled. Viral RNA levels were monitored in northern blot using a GFP probe. Viral genomic and subgenomic RNAs are indicated by arrowheads (top panel). Ethidium-bromide (EtBr) stained gel is shown as loading control (second panel). Virus encoded GFP protein levels were analyzed by western blot (third panel). The same blot was developed with an actin antibody to verify equal loading (bottom panel). (C) Induction of defense related genes in PVX infected plants were monitored by northern blot. RNA samples were prepared from systemically infected leaves at 7 dpi. Samples were pooled from three plants. Actin probe hybridized filter and Ethidium-bromide stained gel are shown as loading controls. Arrowheads indicate PVX genomic and subgenomic RNAs.
