Figure 1.
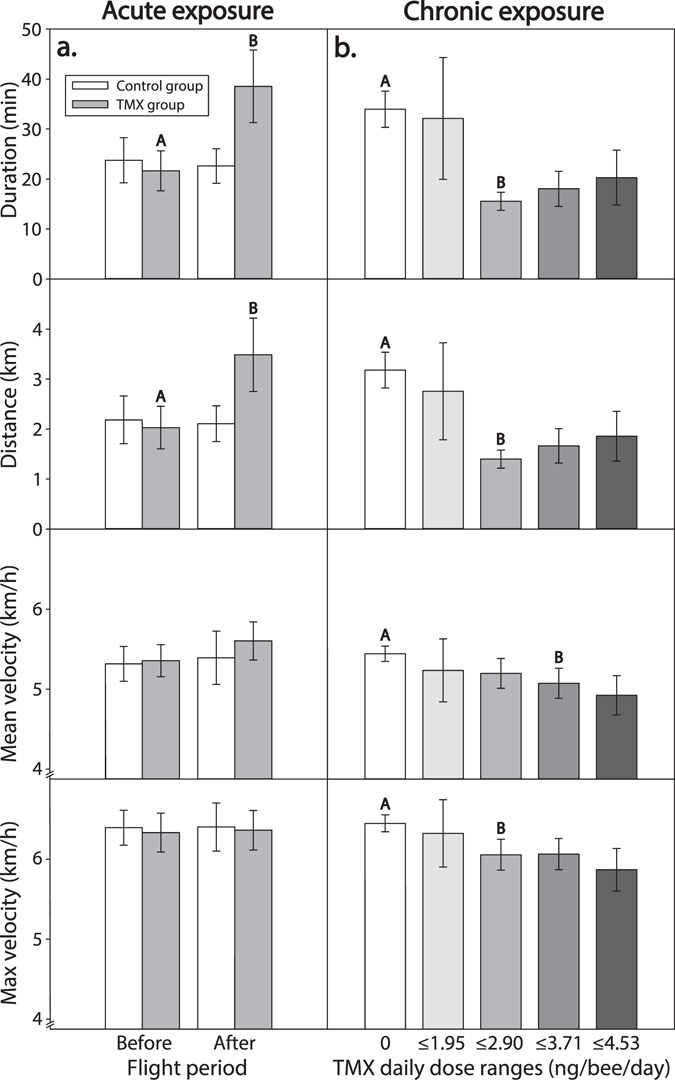
The effects of (a) acute or (b) chronic exposure to thiamethoxam (TMX) on forager flight ability. (a) In the acute experiment, we recorded flight duration, distance, mean velocity and maximum velocity before and after treatment; white bars are the control group ( ), grey bars are the TMX group (
), grey bars are the TMX group ( ); the different letters indicate significant differences (LS Means contrast tests comparing before and after periods; N
control group, before = 16, N
control group, after = 16, N
TMX group, before = 23, N
TMX group, after = 23). (b) In the chronic experiment, we grouped the TMX daily doses (N
TMX daily doses = 46) in 5 TMX daily dose ranges (0, ≤1.95, ≤2.90, ≤3.71, ≤4.53 ng/bee/day). We pooled data from both days of exposure (1 or 2 days) because there was no significant effect of the number of days of exposure. Different shading reflects different daily dose ranges of TMX and different letters indicate significant differences (Least-Square Means contrast tests; N
control = 94, N
32.5 ppb = 44, N
45 ppb = 75). In the x-axis, we report the upper value of each bin range of TMX daily doses. Error bars show standard errors.
); the different letters indicate significant differences (LS Means contrast tests comparing before and after periods; N
control group, before = 16, N
control group, after = 16, N
TMX group, before = 23, N
TMX group, after = 23). (b) In the chronic experiment, we grouped the TMX daily doses (N
TMX daily doses = 46) in 5 TMX daily dose ranges (0, ≤1.95, ≤2.90, ≤3.71, ≤4.53 ng/bee/day). We pooled data from both days of exposure (1 or 2 days) because there was no significant effect of the number of days of exposure. Different shading reflects different daily dose ranges of TMX and different letters indicate significant differences (Least-Square Means contrast tests; N
control = 94, N
32.5 ppb = 44, N
45 ppb = 75). In the x-axis, we report the upper value of each bin range of TMX daily doses. Error bars show standard errors.
