Figure 4.
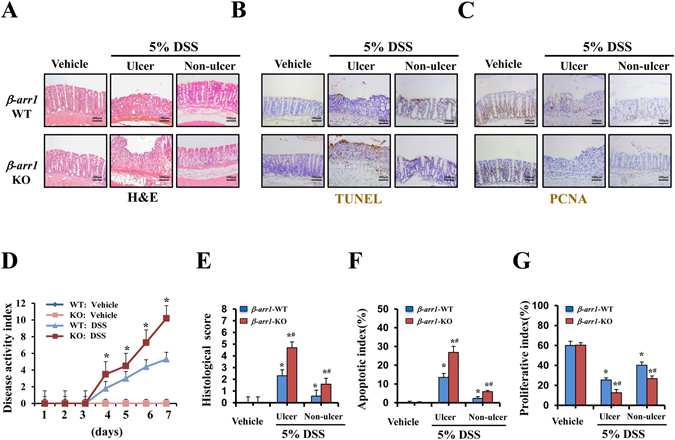
Targeted deletion of β-arr1 exacerbates DSS induced colitis in mice. (A) Representative photomicrographs of H&E staining in colonic sections of β-arr1 WT and KO mice in the control group and the ulcer section and non-ulcer section of the DSS group (×200, n = 4 per group). (B) TUNEL staining revealed apoptotic induction in intestinal epithelial cells of β-arr1 WT and KO mice (brown, ×200, n = 4 per group). (C) Immunohistochemical staining for PCNA in colonic sections of β-arr1 WT and KO mice in the control group and the ulcer section and non-ulcer section of the DSS group. (brown, ×200, n = 4 per group). (D) The disease activity index of mice treated with or without DSS of WT and β-arr1 KO mice was measured at the indicated time points. *P < 0.01 compared with the WT mice (n = 4 per group). (E) Histological damage in colonic tissues obtained from the mice treated with DSS or without DSS of β-arr1 WT and KO mice was scored after H&E staining. *P < 0.05 compared with the control mice, # P < 0.05, β-arr1 WT mice versus KO mice. n = 6 per group. (F) Apoptotic index was measured by quantifying TUNEL signals in 100 random fields per section. Values are expressed as the mean ± SD. n = 6 in each group, *P < 0.05 compared with the control mice, # P < 0.05, β-arr1 WT mice versus KO mice. (G) The percentage of PCNA-positive cells is represented graphically. Values are expressed as the mean ± SD. n = 6 in each group, *P < 0.05 compared with the control mice, # P < 0.05, β-arr1 WT mice versus KO mice.
