Figure 1.
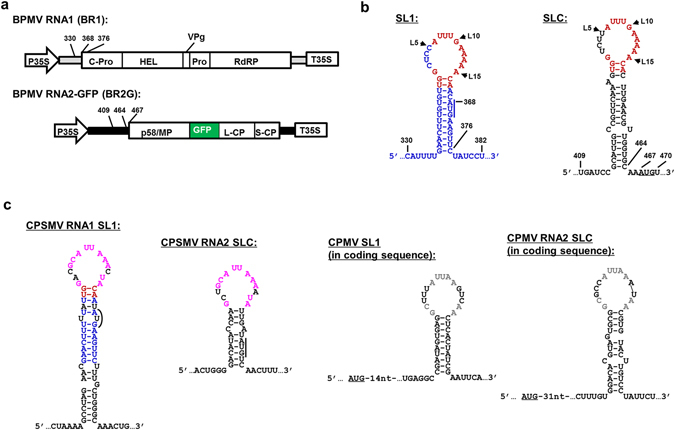
Genome organization of BPMV genomic RNA1 and 2, and the secondary structures of SL1 and SLC in three comoviruses. (a) Diagrams of constructs used to launch BPMV RNA1 (BR1) and RNA2 replication. The RNA2-GFP (BR2G) construct is a derivative of RNA2 cDNA with a GFP insert between MP and L-CP15. Both BR1 and BR2G cDNAs are flanked by the 35S promoter and terminator (P35S and T35S) of cauliflower mosaic virus to facilitate the transcription of viral RNAs by DNA-dependent RNA polymerase II of host cells. Mature viral proteins known to be processed from the polyprotein precursors are represented with varying sized boxes and the corresponding names. The terminal untranslated regions of BR1 and BR2G are depicted as thick gray and black lines, respectively. The numbers near 5′ UTR of BR1 and BR2G delimit the positions of SL1 and SLC, and their intimacy to the polyprotein start codons (also see B). (b) Secondary structures of SL1 and SLC. Nucleotides in blue and black are unique to SL1 and SLC, respectively. Those in red are conserved between SL1 and SLC, which are mostly located within the terminal loops. The AUG start codons of BR1 and BR2G polyproteins are underlined. Note that BR1 AUG is part of the stem of SL1. (c) Putative SL1 and SLC identified in RNA1 and RNA2 of CPSMV and CPMV. Loop nts shared by SL1 and SLC of CPSMV and CPMV are depicted in purple and gray letters, respectively. Note that CPSMV SL1 and BPMV SL1 share 11 base pairs within the stem (red and blue letters). Also note that both SL1 and SLC of CPSMV encompass the AUG start codons, whereas those of CPMV lie shortly downstream of the polyprotein start codons.
