Figure 3.
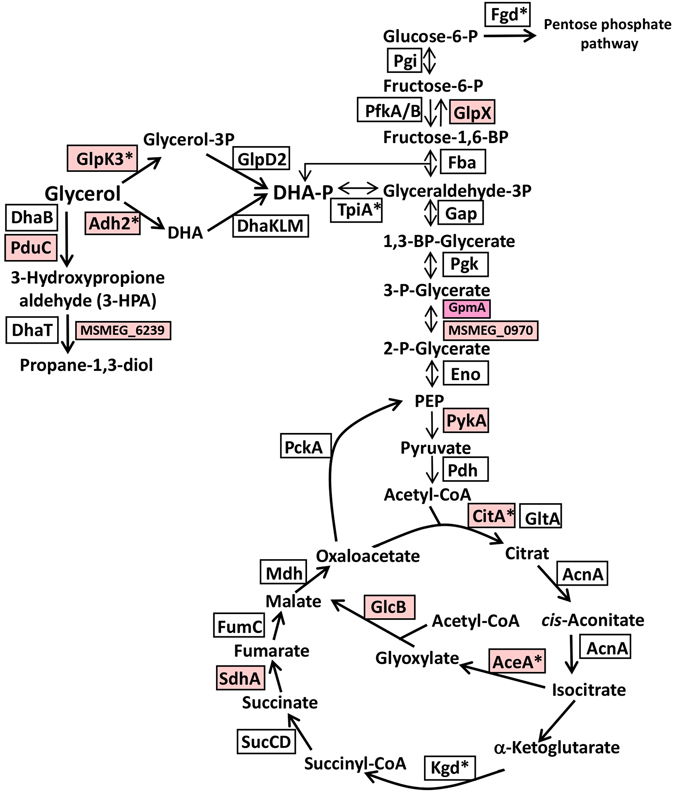
Schematics of the glycerol catabolism, glycolysis, TCA cycle, glyoxylate cycle and gluconeogenesis in M. smegmatis highlighting NaOCl-sensitive thiol-switches. The reversibly oxidized NaOCl-sensitive enzymes are color-coded in light and dark pink indicating 10% and 20% thiol-oxidation increase under NaOCl stress, respectively. The S-mycothiolated proteins are labelled with an asterisk. The pathways of the glycerol catabolism include the aerobic oxidation of glycerol to dihydroxyacetone-phosphate (DHA-P) and the propane-diol-pathway that are catalyzed by (1) the glycerol kinase (GlpK3 or MSMEG_6759) and glyceraldehyde dehydrogenase (GlpD2), (2) the glycerol dehydrogenase (Adh2 or MSMEG_6242) and dihydroxyacetone kinase complex (DhaKLM) and (3) the B12-dependent glycerol dehydratase (DhaB or MSMEG_1546-49) and propane-1,3-diol-dehydrogenase (MSMEG_6239). DHAP enters the glycolysis, TCA and glyoxylate shunt and gluconeogenesis for energy and biomass production. The gluconeogenesis enzymes include GlpX (fructose-1,6-Bis-phosphatase) and PckA (PEP-carboxykinase), while Pgi (glucose-6-phosphate isomerase), Fba (fructose-bisphosphate aldolase), Gap (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase), Pgk (phosphoglycerate kinase), GpmA and MSMEG_0970 (phosphoglycerate mutase) and Eno (enolase) are involved in both glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. The glyoxylate shunt includes the isocitrate lyase (AceA) and malate synthase (GlcB).
