Figure 4.
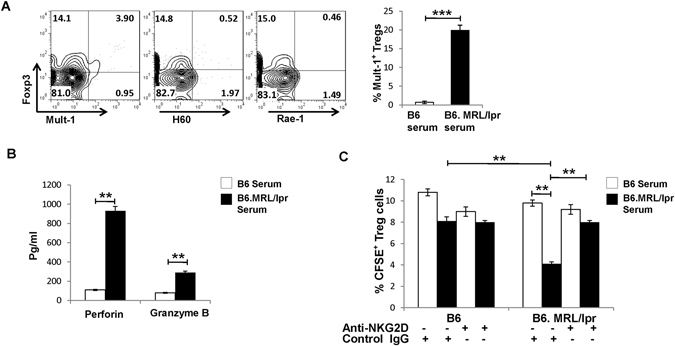
NKG2D+CD4+ T cells killed NKG2DLs-expressing Treg cells in B6.MRL/lpr lupus mice. (A) Induction of NKG2DLs expression on mouse Treg cells by lupus mouse serum. Treg cells isolated from the spleens of C57BL/6 (B6) mice were stimulated with B6 or B6.MRL/lpr lupus mouse serum and then assessed by FCM. Data (left) shown are representative of results from lupus mouse serum. Bar graphs (right) are the statistical results obtained from three independent experiments conducted with 3–5 mice. Numbers represent percentages. (B) Treg cells isolated from the spleens of B6 mice were stimulated with serum from B6 control mice or from B6.MRL/lpr lupus mice and then co-cultured for 6–8 h with NKG2D+CD4+ T cells from B6.MRL/lpr lupus mice. Supernatants were assessed by ELISA. Bar graphs present the statistical results obtained from three independent experiments with Treg cells and NKG2D+CD4+ T cells. (C) CFSE-labeled Treg cells from B6 mice were stimulated in vitro with B6 serum or MRL/lpr mouse serum and transferred to B6 mice and B6.MRL/lpr mice, with or without indicated antibodies pre-treatment, respectively, and the frequency of exogenous Treg cells was examined in gated CD4+ T cells by FCM. Data represent three independent experiments with 3–5 mice. Horizontal lines with vertical bar borders show the mean ± SD. ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001.
