Figure 7.
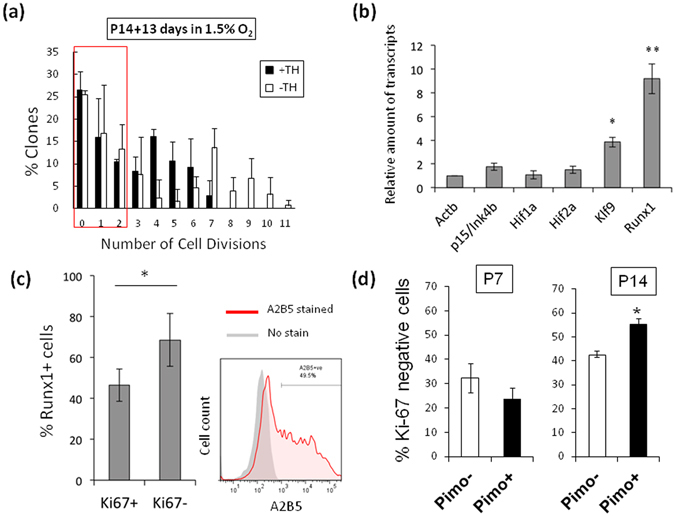
Relevance of adult-like OPCs in culture and adult OPCs in P14 rat optic nerves. (a) Clonal analysis of P14 A2B5+/GC− OPCs cultured at clonal-density in PDGF in 1.5% O2 with TH (black bars) or without TH (white bars). After 13 days, the number of cells in each clone was counted and the number of cell divisions was estimated (n = 3). Around 50% of clones contained the cells of which divided less than two times are shown in red square. (b) P7 OPCs and P14 OPCs were purified from rat optic nerve and their total RNA were prepared immediately. qRT-PCR analysis was carried out. The resulting values were normalized to the endogenous control gene, Actb. Results of P14 OPCs are presented as the relative expression to those of P7 OPCS using the ∆∆Ct methods. *P < 0.001, **P < 0.001 (ANOVA with Fisher’s LSD test, n = 3). (c) GC-negative optic nerve cells prepared from P14 rat were sorted with A2B5 monoclonal antibody (right panel). These GC−/A2B5+ were stained for Runx1 and Ki-67 and examined in immunochemistry. The percentages of Runx1 expressing cells in Ki-67+ or Ki-67− cells are shown (left graph). *P < 0.01 (unpaired Student’s t-test, n = 10). (d) Pimonidazole was injected intraperitoneally into P7 rats or P14 rats. 2 hours later, OPCs were purified from the rat optic nerves. These cells were stained for pimonidazole and Ki-67. The percentages of Ki-67− OPCs that were Pimo− (white bars) or Pimo+ (black bars) at P7 and P14 are shown. *P < 0.001 (unpaired Student’s t-test, n = 4).
