Figure 2.
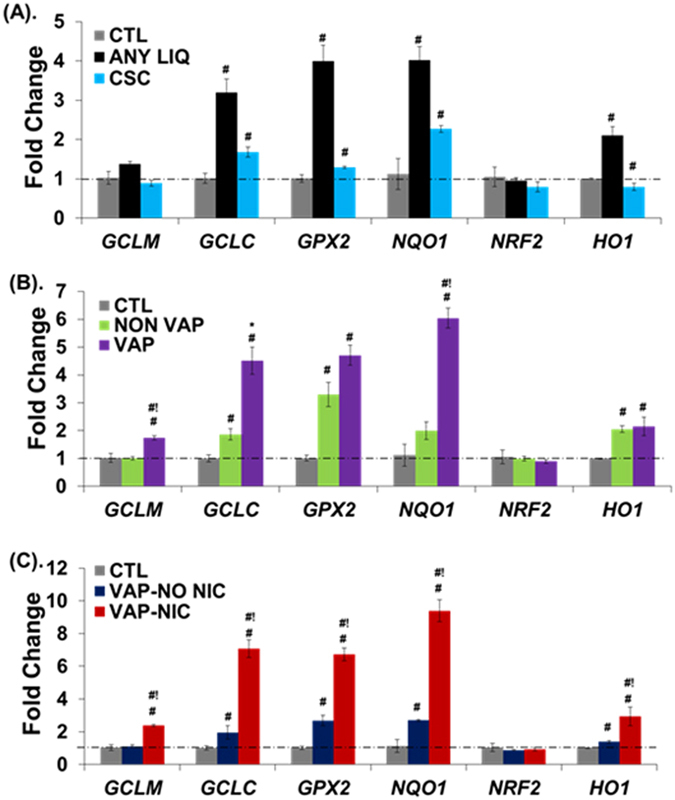
Expression of oxidative stress (OxS) response genes in NHBE cells upon eCig exposure. eCig liquid exposure induces OxS response gene expression in primary human lung epithelial cells. NHBE cells were treated for 2 days with CSC (40 µg), or with 2% non-vaporized (NON VAP) or vaporized and condensed (VAP) eCig liquid, lacking (NO NIC) or containing nicotine (NIC). Following treatment for 48 hours, cells were tested for mRNA expression of OxS genes using qPCR. (A) Treatment of cells with any eCig liquid, vaporized or not, with or without nicotine (ANY LIQ) induced the expression of GCLC, GPX2, NQO1, and HO1. Attenuated responses were observed for CSC. (B) Vaporized and condensed eCig liquid (VAP) displayed a larger response than non-vaporized eCig liquid (NON VAP) on OxS mRNA expression. Treatment of cells with VAP significantly induced the expression of GCLM, GCLC, GPX2, NQO1 and HO1 compared to CTL. Expression of GCLM, NQO1 and GCLC were further increased in VAP treatment compared to NON VAP treated cells. (C) Nicotine containing eCig vapor induced the maximal OxS response among all exposure conditions. VAP with no nicotine (VAP-NO NIC) modestly induced the expression of GCLC, GPX2, NQO1 and HO1 compared to CTL. Conversely, VAP with nicotine (VAP-NIC) induced the expression of GCLM, GCLC, GPX2, NQO1 and HO1 compared to CTL. #p < 0.05 (vs CTL); #!p < 0.05 (NON VAP vs VAP or VAP-NO NIC vs VAP-NIC) (MWU). *p < 0.09 (NON VAP vs VAP) (T-test).
