Figure 1.
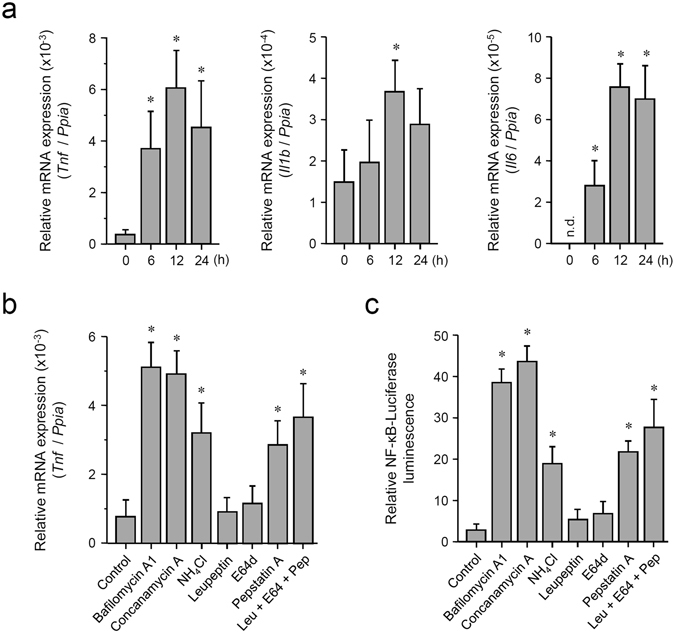
Pharmacological inhibition of lysosomes induces weak inflammatory signals in macrophages. (a) Induction of mRNA of inflammatory cytokines by BafA1 treatment. Mouse BMDMs were incubated with 100 nM BafA1 for the indicated periods, followed by RNA extraction. Relative expression levels of Tnf, Il1b, and Il6 were determined by qRT-PCR. Each value is expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 3); *p < 0.05 (versus 0 h), one-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s test for post-hoc comparisons (μc < μi). n.d.: not detected (regarded as 0). (b) Treatment with the inhibitors of lysosomal functions or lysosomal proteases induces Tnf expression. Mouse BMDMs were incubated with 0.5% DMSO (control), 100 nM BafA1, 100 nM concanamycin A, 20 mM ammonium chloride, 50 μM leupeptin, 50 μM E-64-d, or 2 μM pepstatin A for 12 h, followed by RNA extraction. Relative expression levels of Tnf were determined by qRT-PCR. Each value is expressed as mean ± SD (n = 3); *p < 0.05 (versus Control), one-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s test for post-hoc comparisons (μc < μi). (c) Treatment with the inhibitors of lysosomal functions or lysosomal proteases activates NF-κB-dependent transcriptional activity. The NF-κB-driven luciferase reporter assay was performed in RAW264.7 cells. Cells were incubated with 0.5% DMSO (control), 100 nM BafA1, 100 nM concanamycin A, 20 mM ammonium chloride, 50 μM leupeptin, 50 μM E-64-d, or 2 μM pepstatin A for 12 h. Relative NF-κB activity was measured, and the data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 3); *p < 0.05 (versus Control), one-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s test for post-hoc comparisons (μc < μi).
