Figure 1.
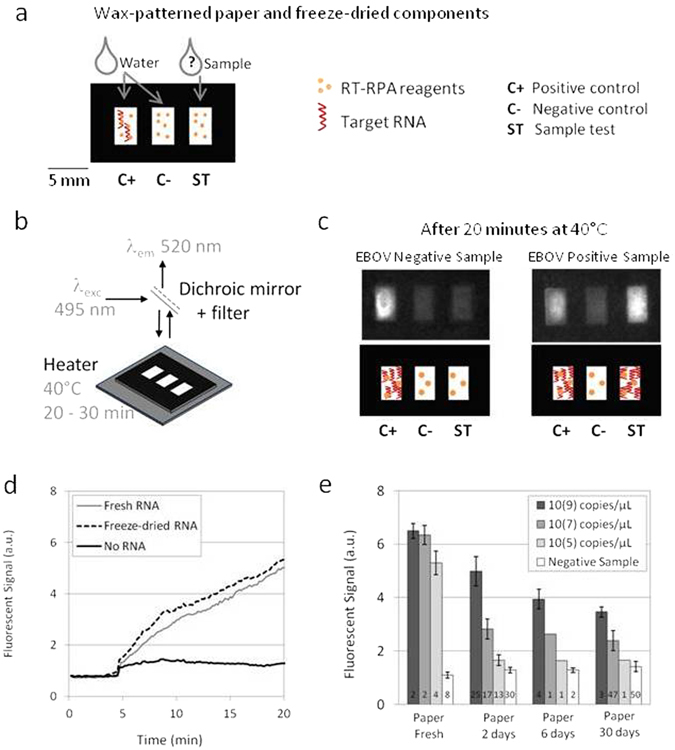
RT-RPA on paper. (a) Wax-patterned geometry on paper and location of freeze-dried RT-RPA reagents and RNA template, rehydrated either with water or the sample. (b) Scheme of the experimental set-up: the paper is put on a heating device and lighted with a 495 nm wavelength; the fluorescent recording at 520 nm is obtained after filtration of the emitted signal. (c) Pictures and scheme of typical results obtained with samples from a healthy donor and an EBOV infected patient, recorded from the experimental set-up presented in (b). (d) Fluorescent signals recording over time for freeze-dried RT-RPA reactions performed on paper and rehydrated with 2.5 µL of distilled water (no RNA - black line), with 2.5 µL of 107copies/µL RNA A (fresh RNA - grey line), with 2.5 µL of distilled water on a zone already containing the same quantities of freeze-dried RNA A (freeze-dried RNA - black dotted line). (e) Compared signal intensities for RT-RPA reactions performed with freshly prepared reagents on paper or with all reagents freeze-dried on paper and stored 2 days, 6 days or 30 days; with various concentrations of target RNA A (dark grey bars: 109, medium grey bars: 107, light grey bars: 105, white bars: 0 copies/µL).
