Figure 4.
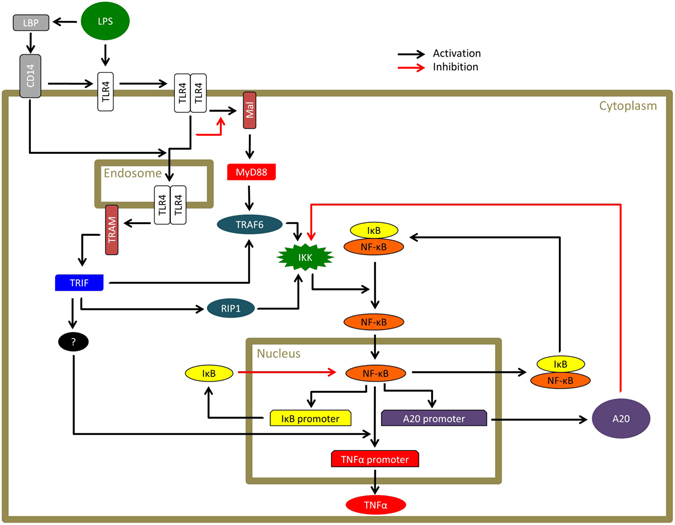
A representative schematic of the proposed TRIF contribution to NF-κB-dependent TNFα promoter activation. LPS activates TLR4 at the cell surface resulting in MyD88 activation via Mal. LPS also promotes TLR4 endocytosis following association with CD14 in the presence of the LPS-binding protein (LBP). TLR4 in the endosome subsequently recruits TRIF via TRAM. TLR4 signalling is transduced sequentially through the MyD88-dependent pathway from the cell membrane and the TRIF-dependent pathway from the endosome. Signals through MyD88-dependent and TRIF-dependent pathways distinctly activate IκB kinase (IKK) via the TNF receptor associated factor 6 (TRAF6) and the kinase receptor interacting protein 1 (RIP1). Activated IKK causes phosphorylation and degradation of IκB followed by NF-κB translocation to the nucleus. In the nucleus, NF-κB activates several promoters. NF-κB requires the cooperation of TRIF-dependent signalling to activate the TNFα promoter. NF-κB also activates promoters of negative regulators including IκB and A20. IκB inactivates NF-κB and leads it to shuttle out of the nucleus. A20 suppresses IKK through inhibition of the upstream signalling.
