Figure 3.
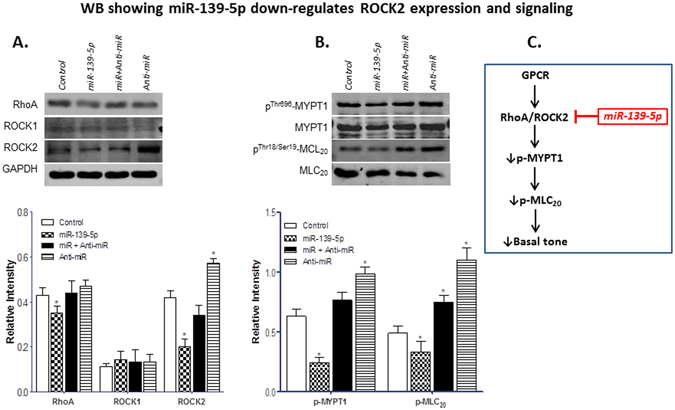
Effect of miRNA-139-5p overexpression on RhoA/ROCK machinery in IAS SMCs. (A) Western blot data showing that miRNA-139-5p overexpression in the IAS SMCs decreases the expression of RhoA/ROCK signal transduction machinery proteins which is selectively blocked by the anti-miRNA-139-5p. (A) (upper portion). Western blots comparing the expression levels of RhoA, ROCK1, and ROCK2 before and after miRNA-139-5p, anti-miRNA-139-5p alone, and following miRNA-139-5p + anti-miRNA-139-5p. The lower portion of the panel provides the corresponding quantitative data showing that miRNA-139-5p causes significant (*p < 0.05) downregulation of RhoA and ROCK2 without any significant (p > 0.05) effect on the levels of ROCK1. Conversely, anti-miRNA-139-5p by itself causes significant upregulation of RhoA and ROCK2 (*p < 0.05). (As indicated, RhoA, ROCK1, and ROCK2 expressions were compared with GAPDH.) (B) (upper portion).Western blots comparing the expression levels of p-MYPT1and p-MLC20, before and after miRNA-139-5p, anti-miRNA-139-5p alone, and following miRNA-139-5p + anti-miRNA-139-5p. The lower portion of this panel provides the quantitative data showing that miRNA-139-5p significantly (*p < 0.05) downregulates, while anti-miRNA-139-5p causes significant (*p < 0.05) upregulation of p-MYPT1 and p-MLC20. (As shown, p-MYPT1, and p-MLC20 expressions were compared with MYPT1 and MLC20, respectively.) (C) Model representing the effect of miRNA-139-5p on RhoA/ROCK2 signaling cascade. The IAS smooth muscle is characterized by upregulated RhoA/ROCK signaling which may be either constitutively active or GPCR-activated. Data suggest that higher levels of miRNA-139-5p in the IAS attenuate ROCK2 expression, which in turn leads to activation of MLCP (via decrease in p-MYPT1), and decrease in p-MLC20 and basal tone.
