Figure 4.
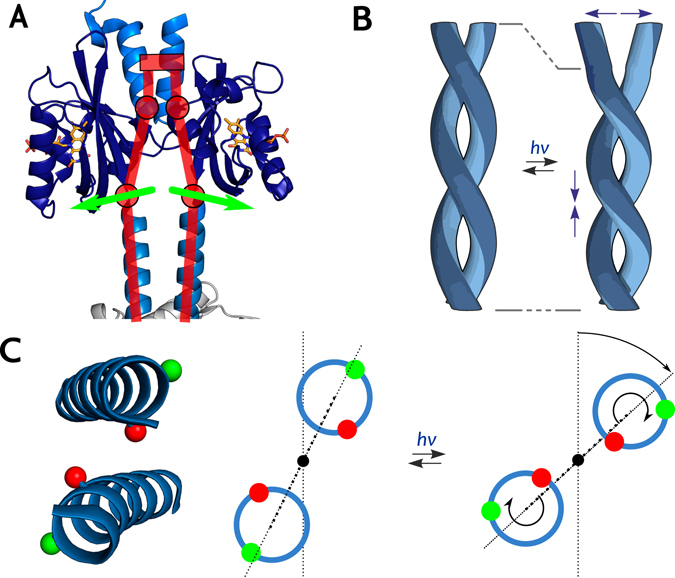
Schematic of the transition from dark-adapted to light-adapted state of YF1 and proposed signal transduction mechanism. (A) The outward tilt of the LOV domains in a hinge-like motion (red) causes separation of the N-termini of the coiled-coil linker (green arrows). (B) Separation of the N-termini would induce torque and left-handed supercoiling of the coiled-coil linker. (C) As a result, the C-termini of the linker helices (inset) would be rotated relative to the C2 axis of the coiled coil, causing both a rotation of the LOV dimer relative to the histidine kinase effector (dotted line) and an angular movement of the helices themselves. To illustrate the resultant angular displacement, within each helix two positions separated by one residue are highlighted in green and red, respectively.
