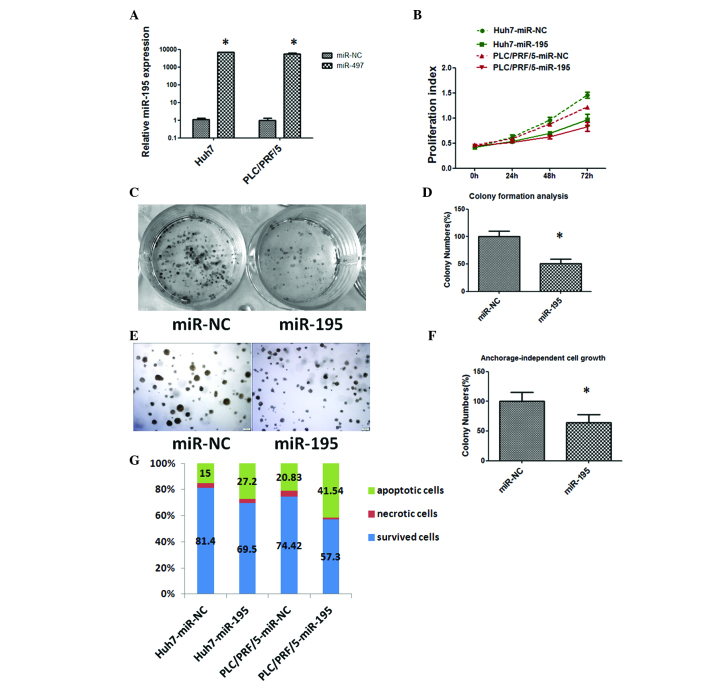
Figure 2.
Tumor suppressive effects of miR-195 in hepatocellular carcinoma. (A) Relative expression of miR-195 in Huh7 and PLC/PRF/5 cells was detected by reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction at 48 h following transfection of the cells with 50 nM miR-195 mimics or miR-NC. The average miRNA expression level from the miR-NC group was designated as 1. (B) Overexpression of miR-195 suppressed the proliferation of Huh7 and PLC/PRF/5 cells. (C) miR-195 overexpression decreased the colony-forming ability of Huh7 cells. (D) A histogram indicated that miR-195 inhibited colony formation. The percentage of colony numbers of the miR-NC group was designated as 100%. (E) Restoration of the expression of miR-195 inhibited the anchorage-independent cell growth ability of Huh7 cells. (F) A histogram indicated that miR-195 inhibited anchorage-independent cell growth. The percentage of colony numbers of the miR-NC group was designated as 100%. (G) miR-195 induced apoptosis. Apoptosis was detected by Annexin V/propidium iodide staining combined with flow cytometry in Huh7 and PLC/PRF/5 cells at 48 h subsequent to transfection. Apoptotic evaluation was determined by the percentage of apoptotic cells out of the total cell number. *P<0.05. miR-195, microRNA-195; miR-NC, negative control microRNA.