Figure 8.
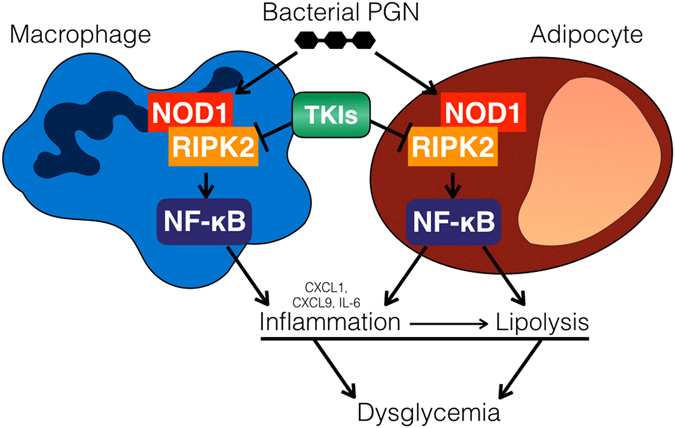
Inflammatory and metabolic effects of TKIs that inhibit RIPK2 in adipocytes and macrophages. RIPK2 is required for increased inflammatory cytokine production and lipolysis induced by bacterial peptidoglycan that acts on NOD1. Certain tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) inhibit RIPK2 in both macrophages and adipocytes thereby suppressing lipolysis, reducing inflammation and attenuating poor glucose control (dysglycemia) caused by bacterial cell wall components.
