Figure 1.
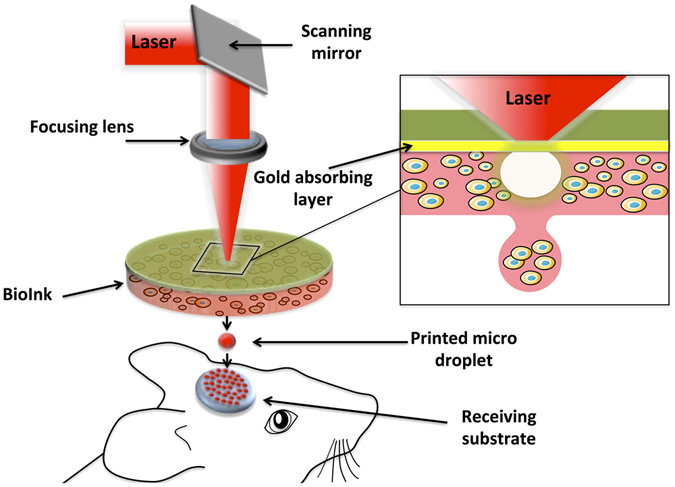
Schematic representation of the laser assisted bioprinting (LAB) approach. A typical LAB setup comprises a pulsed laser beam, a focusing system, a ribbon (a transparent glass slide, coated with a laser-absorbing layer of metal, onto which a thin layer of bioink is spread, and a receiving substrate facing the ribbon. The physical principle of LAB is based on the generation of a cavitation-like bubble, into the depth of the bioink film, whose expansion and collapse induces the formation of a jet and, thereby, the transfer of the bioink from the ribbon to the substrate (here a bone defect on the mouse calvaria), forming a microdroplet.
