Figure 3.
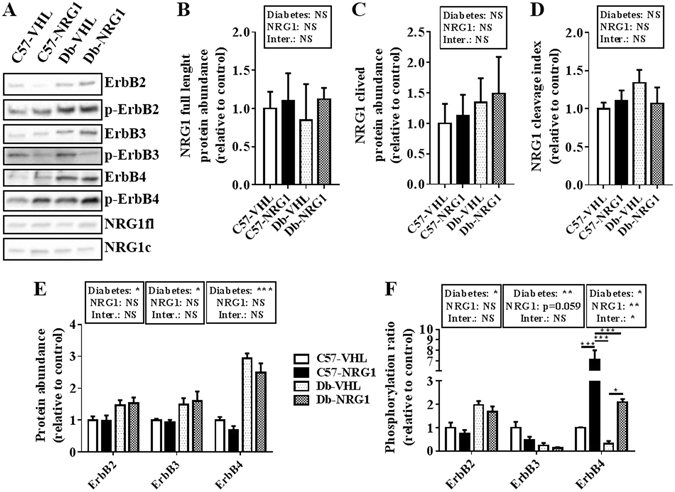
NRG1 treatment increases ERBB4 activation in gastrocnemius muscle. C57BL/6JRJ (C57) control and db/db (Db) male mice were treated with vehicle (VHL; 0.9% NaCl solution; n = 8/each condition), or with NRG1 (50 μg . kg−1; n = 8/each condition), three days per week for eight weeks. Western blot analysis (A) cropped images) was used to quantify in gastrocnemius muscle samples the abundance of full length (115 kDa) (B) and cleaved (42 kDa) (C) NRG1 and the NRG1 cleavage index (the ratio between cleaved and full length NRG1) (D) as well as the abundance (E) and phosphorylation ratios (F) of ERBB2, ERBB3 and ERBB4. Results are the mean ± SEM (n = 8 per group) relative to the level in untreated healthy mice (C57-VHL, white bars). Diabetes (healthy vs db/db mice) and NRG1 (saline vs NRG1) effects were investigated with a 2 × 2 ANOVA. When a significant interaction was found, the Tuckey’s test was used for post-hoc multiple comparisons. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, NS: not significant.
