Figure 1.
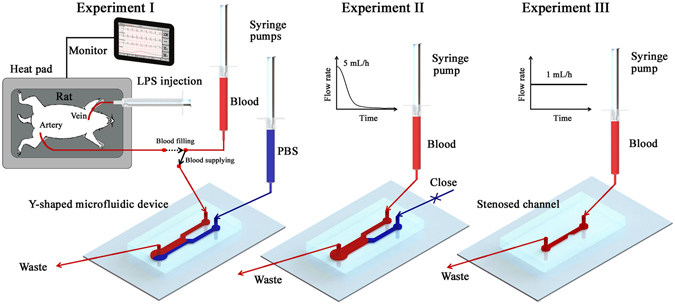
Measurement procedure of the microfluidic system for monitoring blood viscosity, RBC aggregation and platelet adhesion. A rat extracorporeal conduit is established by connecting the artery of a rat and a microfluidic conduit. By manipulating a three-way valve, blood in the rat artery is filled in the syringe and supplied into the microfluidic devices. Viscosity of blood sample is measured by inducing an interfacial line between a reference PBS solution and test blood sample in the Y-shaped microfluidic device (Experiment I). After measuring viscosity variation according to shear rate, Experiment II is carried out to measure RBC aggregation while the inlet of PBS solution is closed. Flow rate of test blood sample is reduced from 5 mL/h to 0 mL/h to induce the formation of RBC aggregates. For the estimation of platelet adhesion, Experiment III is performed by connecting a microfluidic channel with stenosis (90% severity) into the rat extracorporeal conduit. Flow rate of the blood sample is maintained at 1 mL/h during Experiment III.
