Figure 4.
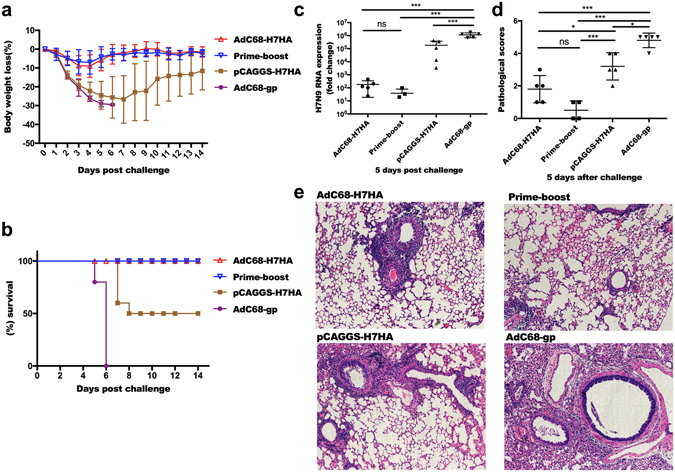
A single immunization with AdC68-H7HA or DNA prime-adenovirus boost regimen protected mice from lethal H7N9 viral challenge. Eight weeks after immunization, mice were challenged with 3.5 × 105 TCID50 of H7N9 virus, after which body weights and survival rates were monitored for 14 days. (a) Body weight changes. (b) Survival rates. No significant difference was observed between the prime-boost group and the AdC68-H7HA group. Results of the prime-boost group and the AdC68-H7HA group were significantly different compared with those of the AdC68-gp group (p = 0.00001) and the DNA-only group (p = 0.03). (c) H7N9 viral loads in mouse lungs at 5 days post-challenge. Five days after challenge, the mice were sacrificed and the lungs were harvested and homogenized to extract the total RNA. Then, real-time PCRs were performed. (d) Pathological scores of the lungs at 5 days after challenge. (e) Lung sections were stained with H&E to assess inflammation and tissue damage on day 5 after challenge. The error bars represent the SD. ***p < 0.001; **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05; ns, not significant.
