Figure 3.
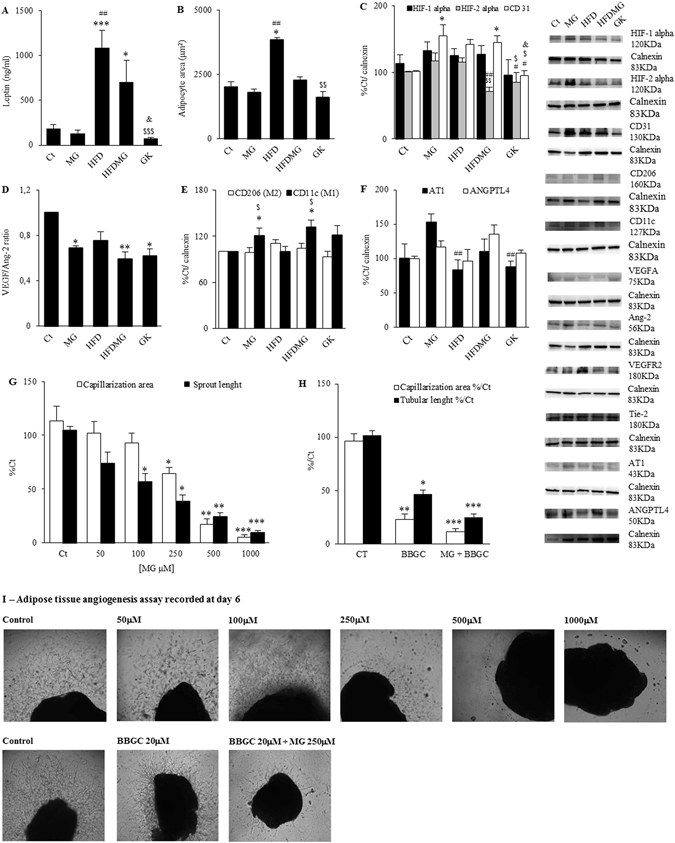
Glycation hampers adipose tissue pathways of adaptation to hypoxia, angiogenesis and expandability ratio. Serum leptin levels were assessed by ELISA (A). Adipocyte area was evaluated through the number of adipocytes counted in each field (10 fields/rat) (B). The levels of HIF-1alpha, HIF-2alpha, CD31 (C), VEGF, Ang-2 (D), CD11c, CD206 (E) ANGPTL4 and AT1 (F) were determined by WB. The VEGF/Ang-2 ratio was calculated. The adipose tissue angiogenesis assay was used to evaluate the effects of glycation in adipose tissue angiogenesis. MG concentrations higher than 100 μM decreased vascularization area, while lower concentrations decreased sprout length (G). Glyoxalase-1 inhibitor BBGC reduced vascularization area and sprout length, an effect which was further increased in combination with MG exposure (H). Representative images of all conditions are shown in (I). Ct - Wistar 12 m; MG - Wistar + MG supplementation; HFD - HF diet-fed Wistar; HFDMG - HF diet-fed Wistar + MG supplementation; GK - Goto-Kakizaki 12 m. Bars represent means ± SEM, n = 6–8. * vs Ct; # vs MG; $ vs HFD; & vs HFDMG; 1 symbol p < 0.05; 2 symbols p < 0.01; 3 symbols p < 0.001.
