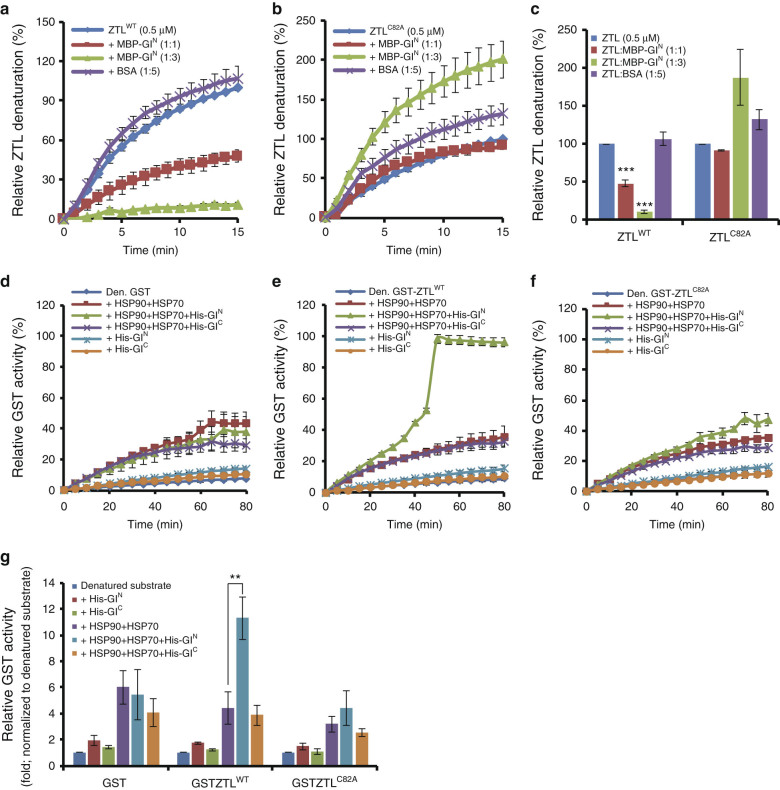
Fig. 2.
ZTL is a specific client of GI N chaperone activity in vitro. a MBP-GIN decreases heat-mediated ZTLWT aggregation with increasing levels of MBP-GIN. b MBP-GIN has no effect or increases heat-mediated aggregation of the ZTLC82A allele. c The mean denaturation state at the treatment endpoint of a and b relative to thermal-denaturation of ZTLWT or ZTLC82A alone. BSA used as a non-specific protein control. Holdase activity of MBP-GIN was measured as the change in turbidity at 340 nm (aggregation of ZTLWT or ZTLC82A (0.5 μM)) under thermal denaturing conditions (45 °C) for 15 min. The value of ZTLWT or ZTLC82A alone at 15 min was set to 100%, and turbidity at 340 nm from each treatment expressed relative to it. BSA used as a non-specific protein control. d–f GI acts synergistically with HSP90 and HSP70 to reactivate denatured GST-ZTL. d GST, e GST-ZTLWT, and f GST-ZTLC82A were heat-denatured at 45 °C and immediately mixed with His-GIN (0.05 μM) or His-GIC (0.05 μM) in the absence or presence of HSP90 (0.1 μM) and HSP70 (0.5 μM). Enzyme activity of undenatured GST, GST-ZTLWT, and GST-ZTLC82A was set to 100% for d, e and f, respectively. g Mean GST activity at the treatment endpoint of d–f was normalized to the spontaneously refolding value of denatured GST or GST-fusions set to 1. The foldase assay determined GST activity by measuring the formation of a GS-DNB conjugate (GST reaction product) as determined by absorbance at 340 nm (Abs340). **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; two-tailed Student’s t-test. Data are means ± s.e. (n = 3)