Figure 2.
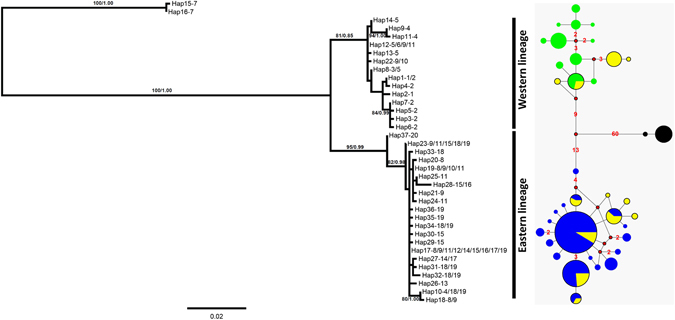
Maximum likelihood (ML) tree and the median-joining network derived from cytochrome b partial sequences of B. tibetanus sampled in the Qinling Mountains. The haplotypes are named by numbers (1–37). Haplotype shared by multiple locations are labelled by all location numbers separated by ‘/’. Haplotype and location numbers are separated by ‘−’. The two haplotypes (Hap15 and Hap16) from QLC population are the Tibetan lineage of B. tibetanus distributed in the Qinling Mountains (Supplementary Fig. S1), and are considered to be outgroup to explore phylogenetic relationship among the Qinling lineages. The Qinling lineages were previously described as B. taibaiensis 35. Numbers next to nodes of ML tree indicate bootstrap values and Bayesian posterior probabilities. Numbers in network represent the mutation steps. Sizes of circles are proportional to the haplotype frequencies. Colours for populations: green, the western group; blue, the eastern group; yellow, populations possessing haplotypes from both lineages; black, the QLC population.
