Figure 6. Modular regulatory architecture characterizes color pattern diversity within the Heliconius erato radiation.
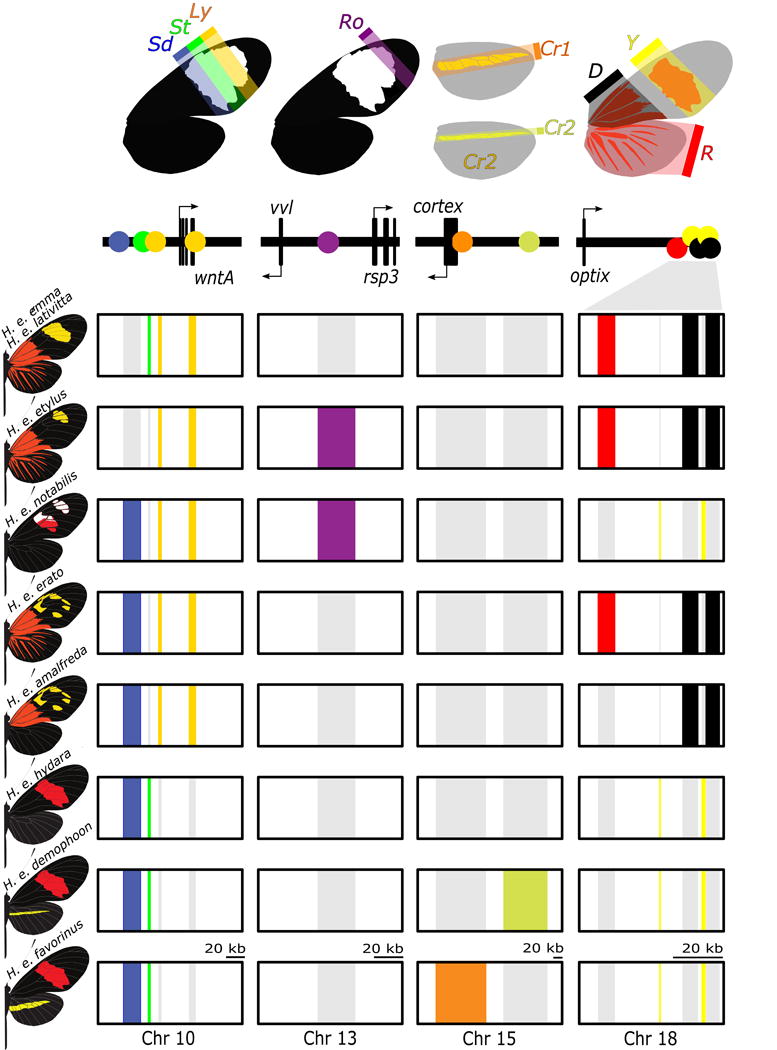
The upper panel provides a summary of color pattern variation found among H. erato butterflies that is related to spatial expression of the genes wntA (black forewing patterning; chromosome 10), cortex (yellow hindwing bar; chromosome 15), optix (red; chromosome 18) and a functionally uncharacterized genomic interval on chromosome 13 responsible for pattern variation in the most distal region of the forewing band (Ro; functional candidates vvl and rsp3). The boxes in the bottom panel represent chromosomal intervals that include regulatory modules. These regulatory modules are colored for butterflies in which the pattern is expressed. The regulatory modules have been rearranged among H. erato races to generate distinct wing phenotypes. Note that for Cr1 and Cr2 and rays (R), band (Y) and dennis (D) patterns are expressed when, respectively, cortex and optix are expressed, whereas for Sd, St and Ly pattern expression corresponds with absence of wntA expression.
