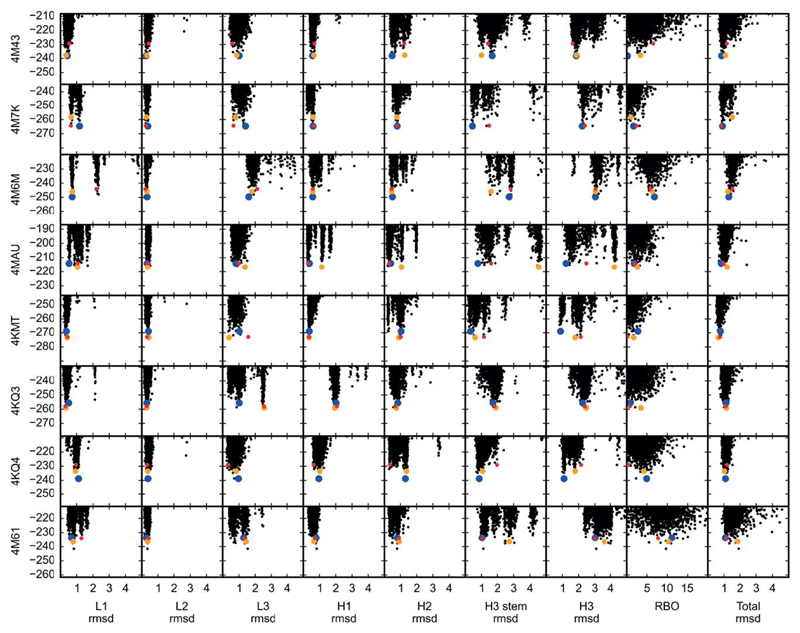
Figure 2.
Combinatorial-backbone modeling in AbPredict explores the energy landscape discretely. Unlike ab initio methods,3,11–13 combinatorial backbone modeling as implemented in AbPredict only explores combinations of conformations, which are observed in natural structures; since these conformations fall into clusters,2 the resulting energy landscape in AbPredict is more discrete than seen in ab initio methods. The rigid-body orientation between light and heavy chains (RBO) is a more continuous degree of freedom, and accordingly the energy landscape for RBO is less discrete than that of the backbone conformations. Carbonyl rmsd or RBO deviation from the experimental antibody structure is measured on the x axis, and energy (in Rosetta energy units) on the y axis. The lowest-energy model of the most, the second most, and the third most populated clusters are automatically selected (see Methods) and are marked by blue, yellow, and red, respectively.