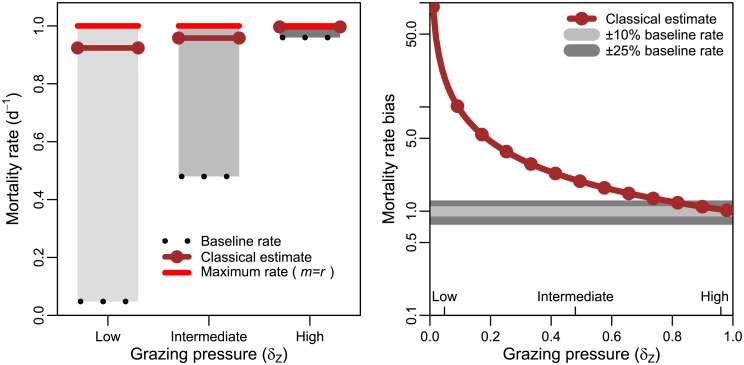
Fig 2. The classical dilution method may overestimate rates of mortality via grazing.
(A) Expected baseline microzooplankton associated mortality rates and rates estimated using the classical dilution method for three levels of grazing pressure; low grazing pressure (1000 microzooplankton ml−1), intermediate grazing pressure (10000 microzooplankton ml−1) and high grazing pressure (20000 microzooplankton ml−1). The maximum mortality rate is calculated for the condition when total mortality, m, is equal to the phytoplankton growth rate r. (B) Mortality rate bias across the full gradient of grazing pressure. The grazing pressure associated with each of the examples given in (A) are shown on the x-axis.