Figure 7. The phenotype of the gain of function mutant of arl-8.
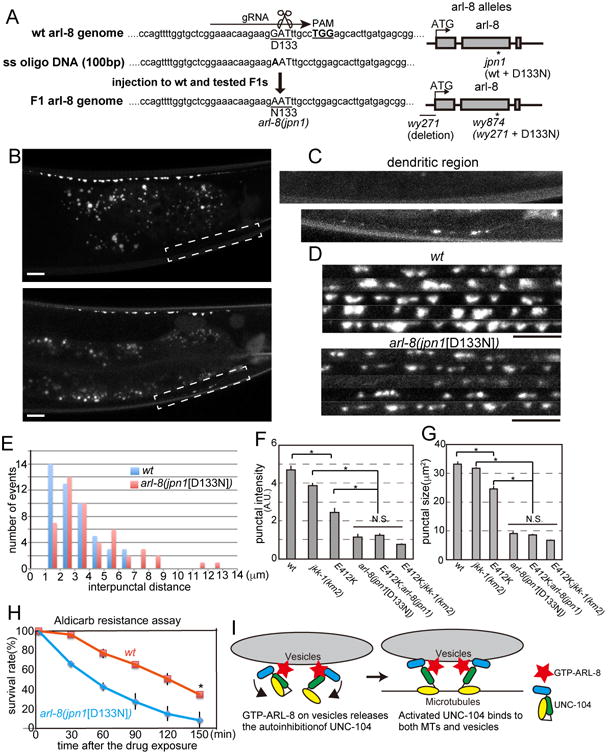
(A) Left, Genome editing using the CRISPR/CAS9 method. The D133N mutation was introduced into the wild type background to generate an arl-8 allele, arl-8(jpn1). Right, a schema showing the genomic structure of arl-8(jpn1), arl-8(wy271) and arl-8(wy874) (B-D) Representative confocal images of wild type and arl-8 (jpn1[D133N]). (B) Gross phenotype. (C) The dendritic mislocalization. and (D) Image montages of part of the synaptic region in WT and arl-8(jpn1[D133N]). Scale bars, 10 μm.
(E) The distribution of the interpunctal distance in wild type (WT) and arl-8(jpn1). In arl-8(jpn1), the mean intersynapse distance is significantly longer compared to wild type. (p < 0.01, Mann-Whitney U test, n = 50 intersynapses from 3 animals).
(F and G) Characterization of synaptic boutons in wild type, jkk-1, unc-104(wy798), arl-8(jpn1), unc-104(wy798);arl-8(jpn1) double mutant and unc-104(wy798); jkk-1 double mutant visualized by RAB-3∷GFP. Punctal intensity and size were measured as described in Figure 4. Mean ± SEM, p < 0.01, Dunnett test, n = 60 synaptic boutons.
(H) The aldicarb resistance assay. arl-8(jpn1) is resistant to the aldicarb treatment compared to wild type. Mean ± SD. *, p < 0.05, compared to wt at 150 min, t-test. Three independent experiments. 25 worms were tested in each experiment.
(I) A model showing how UNC-104 is activated. GTP-ARL-8 on vesicles strongly binds to the stalk domain of UNC-104 and releases the autoinhibition. Activated UNC-104 can bind to both MTs and SVs. See also Figure S5.
