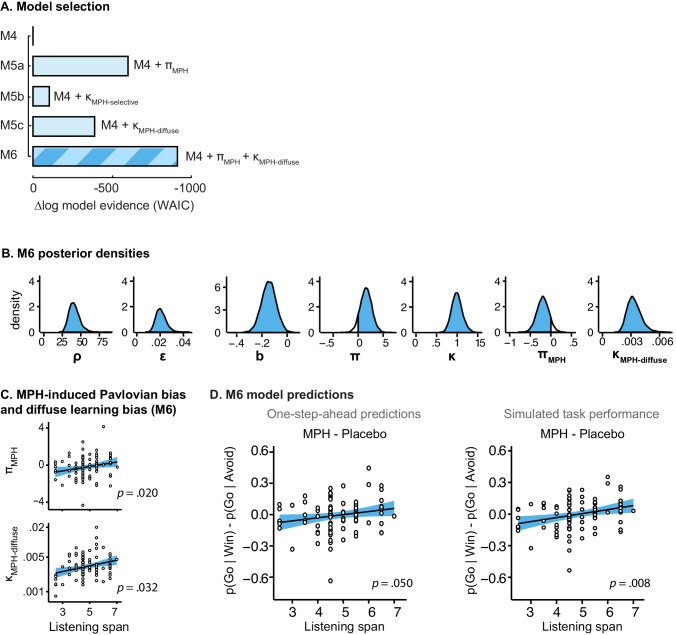
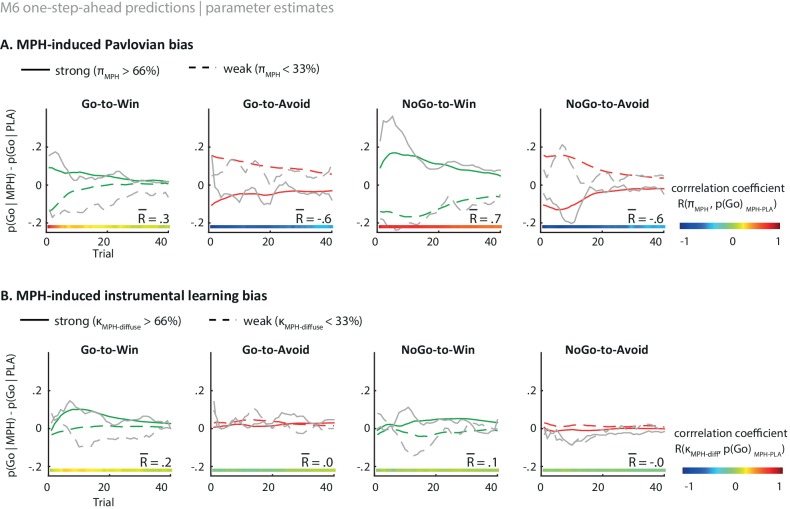
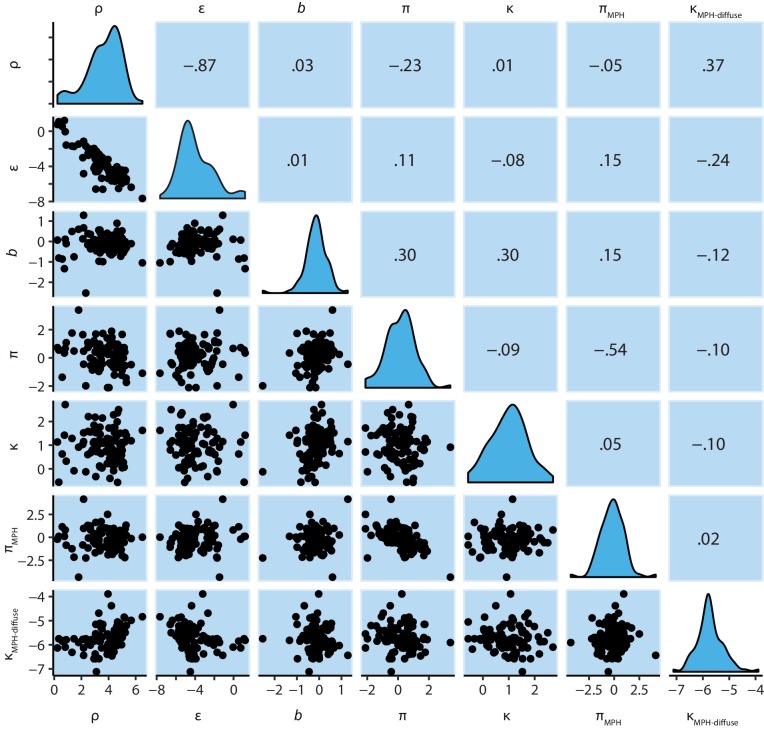
Figure 5. Model evidence and parameter inference of extended MPH models.
(A) Model evidence (WAIC) relative to winning base model M4. We tested whether MPH alters the strength of the Pavlovian response bias (πMPH; M5a), the instrumental learning bias (κMPH-selective; M5b), or has a diffuse effect on the learning bias (κMPH-diffuse; M5c; Figure 1C). Model selection favoured the composite model M6, including the πMPH and κMPH-diffuse parameters. (B) Posterior densities of the top-level parameters of M6. (C) Subject-level estimates of MPH-induced Pavlovian bias parameter (upper) and the MPH-induced diffuse learning bias parameter (lower; logistic scale) correlated significantly with Listening Span. (D) One-step-ahead model predictions and posterior predictive model simulations of M6 using subject-level parameter estimates. The model predictions and simulations echo the observed data, i.e. that the motivational bias correlates positively with working memory span (Figure 4B), confirming the winning model M6 captures the MPH-induced increase in Go responses to Win vs. Avoid cues.