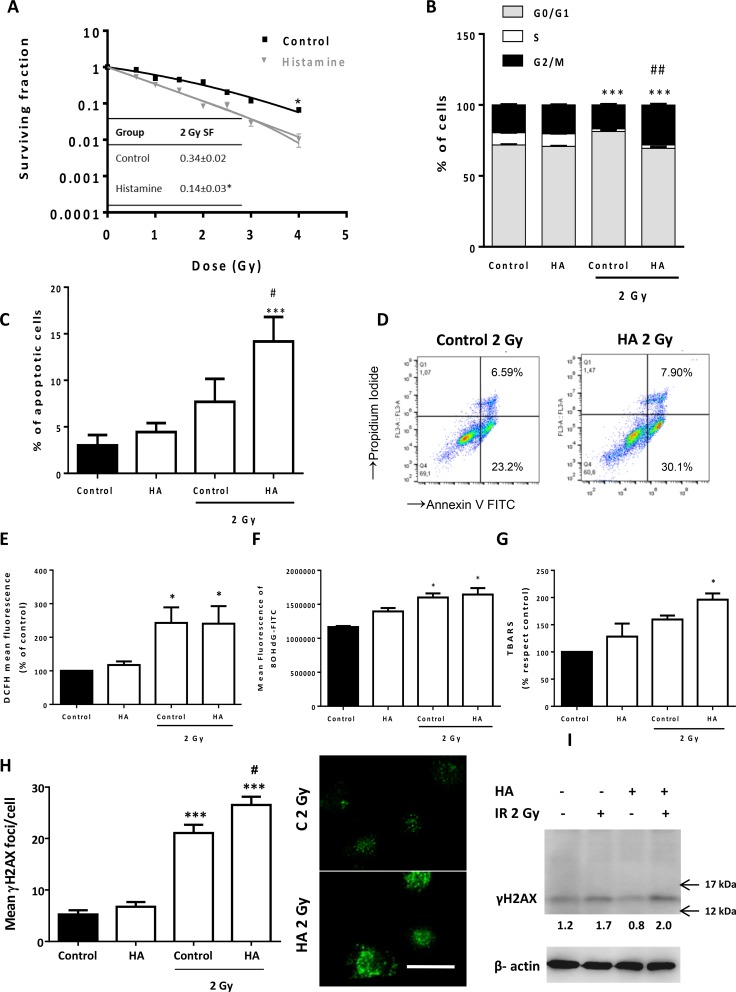
Figure 6. Effect of histamine on the radiosensitivity of melanoma cells.
1205Lu cells were cultured in presence or absence of histamine (HA) and were irradiated 24 h after treatment. (A) Clonogenic survival was determined. Radiobiological parameters of 1205Lu cells were obtained from the survival curves adjusted to the linear quadratic model [SF= e−(αD+βD2)]. Values are means ± SEM of 3 independent experiments performed in triplicates. Inset: 2 Gy SF of untreated and histamine-treated cells. (B) The percentage of cells in different phases of the cell cycle was monitored 24 h after irradiation using flow cytometry. Results represent the mean value of 3 independent experiment (***P < 0.001 vs. % S phase of Control; ##P < 0.01 vs. % G2/M phase of 2 Gy Control. ANOVA and Newman-Keuls post test). (C) Percentage of apoptotic cells was determined 24 h after irradiation by the TUNEL assay (***P < 0.001 vs. Control; #P < 0.05 vs. 2 Gy Control. ANOVA and Newman-Keuls post test), and by (D) Annexin-V staining and flow cytometry. Annexin-V positive cells are shown in both right quadrants of dot plot. (E) Measurement of intracellular ROS by flow cytometry (*P < 0.05, ANOVA and Newman-Keuls post test). (F) Mean fluorescence analysis of 8-OHdG determined by flow cytometry (*P < 0.05 vs. Control, ANOVA and Newman-Keuls post test). (G) Percentage of thiobarbituric acid reactive species (TBARS) with respect to untreated cells (control), (*P < 0.05 vs. Control, ANOVA and Newman-Keuls post test). (H) DNA double strand breaks were evidenced by γH2AX foci formation. The average number of foci per cell was determined 20 min after irradiation. Representative pictures were taken at a 400X-fold magnification (Scale bar = 20 μm). (I). γH2AX (15 kDa) was assayed by Western blot. β-actin (42 kDa) was used as loading control. Semiquantitative analyses of band intensities are shown (n = 3).