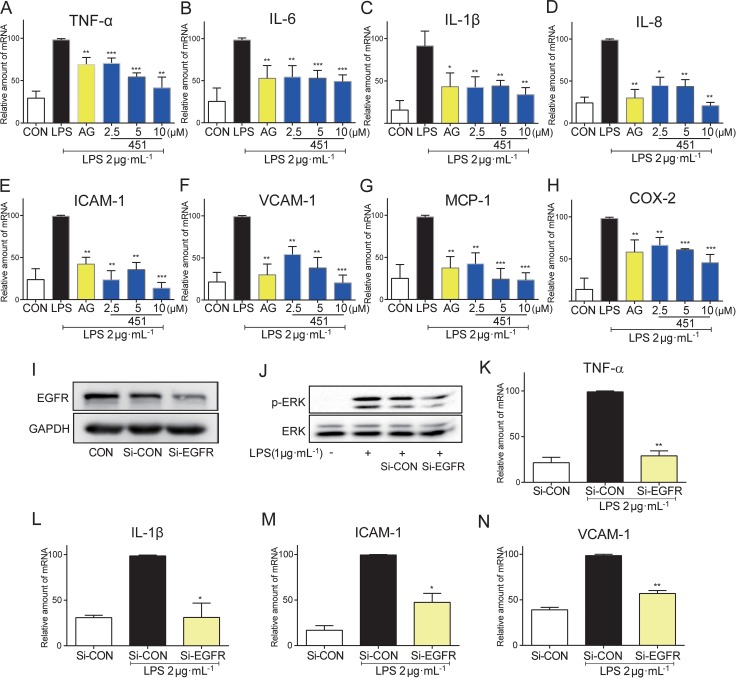
Figure 2. EGFR inhibition reduced the LPS-induced inflammation in BEAS-2B.
(A–H) BEAS-2B cells were pre-treated with AG1478 at 10 μM or 451 at various doses (2.5, 5, 10 μM) or vehicle (DMSO) for 30 min prior to stimulation with LPS (2 μg·mL−1) for 12 h. Total mRNA was extracted from the cell using TRIzol and the mRNA levels of TNF-α (A), IL-6 (B), IL-1β (C), IL-8 (D), ICAM-1 (E), VCAM-1 (F), MCP-1 (G) and COX-2 (H) were detected by real-time RT-qPCR analysis. (I) Western Blot shows EGFR knockdown efficiency following EGFR siRNA (Si-EGFR) transfection in BEAS-2B cells as measured by EGFR protein levels (CON: non transfected cells; Si-CON: non-EGFR scrambled transfection cells). (J) Effects of EGFR knock-down by siRNA on ERK phosphorylation in BEAS-2B cells stimulated with 1 μg/mL LPS. (K–N) Effects of EGFR knock-down by siRNA on inflammatory cytokines TNF-α (K) and IL-1β (L), and adhesion molecular ICAM-1 (M) and VCAM-1 (N) mRNA expression in BEAS-2B cells stimulated with 2 μg·mL−1 LPS. Bars represent the mean ± SEM of more than three independent experiments performed in duplicate, and asterisks indicate significant inhibition (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001, vs. LPS group).