Abstract
The size of synaptic quanta has been found to display considerable variation in cultured hippocampal neurons, but the source of this variability was previously unknown. We have now compared the properties of locally evoked miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents in cultured hippocampal neurons and in thin hippocampal slices using whole-cell patch-clamp recordings. The variability in miniature excitatory postsynaptic current size was similar in both preparations and occurred in cultured neurons when only one or a few synaptic boutons were stimulated. Thus, the variability in miniature excitatory postsynaptic current amplitude is not an artifact of cultured neurons and arises predominantly from variability within a single bouton. Possible origins of this variability are discussed.
Full text
PDF
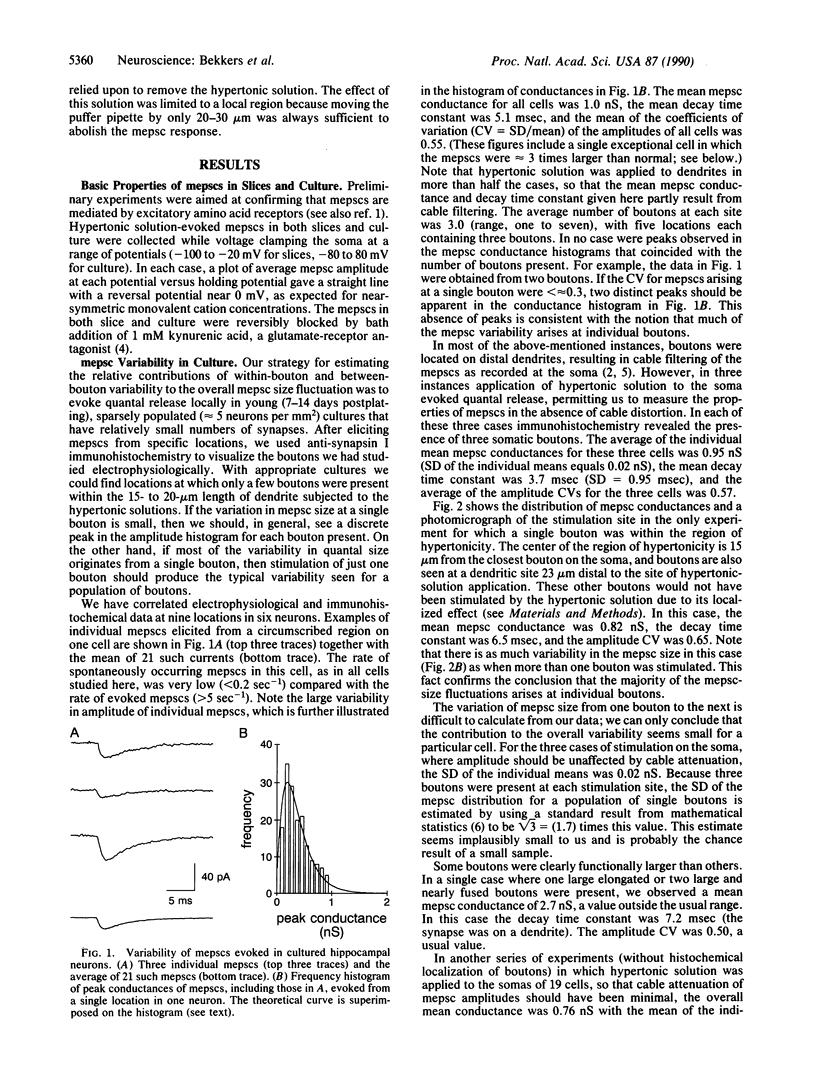
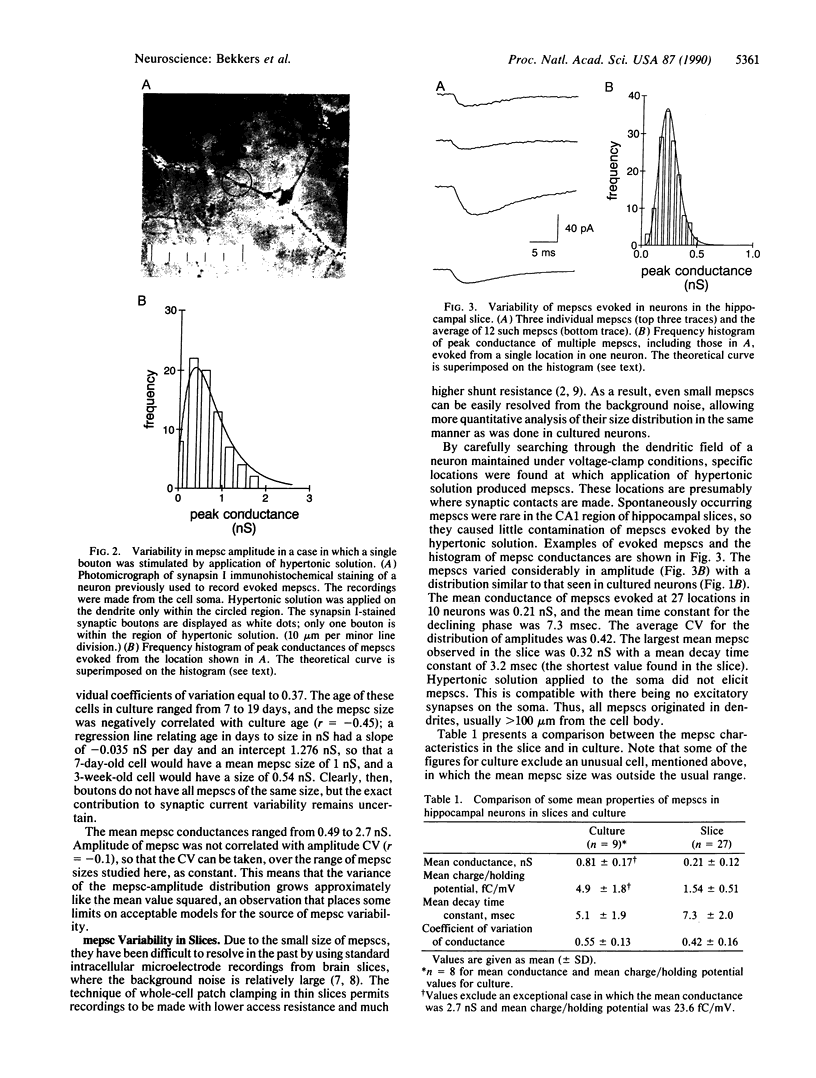

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bekkers J. M., Stevens C. F. NMDA and non-NMDA receptors are co-localized at individual excitatory synapses in cultured rat hippocampus. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):230–233. doi: 10.1038/341230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. H., Wong R. K., Prince D. A. Spontaneous miniature synaptic potentials in hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1979 Nov 9;177(1):194–199. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90931-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards F. A., Konnerth A., Sakmann B., Takahashi T. A thin slice preparation for patch clamp recordings from neurones of the mammalian central nervous system. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Sep;414(5):600–612. doi: 10.1007/BF00580998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froesch D. A simple method to estimate the true diameter of synaptic vesicles. J Microsc. 1973 May;98(1):85–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1973.tb03807.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins M. N., Stone T. W. An iontophoretic investigation of the actions of convulsant kynurenines and their interaction with the endogenous excitant quinolinic acid. Brain Res. 1982 Sep 9;247(1):184–187. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)91048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sah P., Hestrin S., Nicoll R. A. Tonic activation of NMDA receptors by ambient glutamate enhances excitability of neurons. Science. 1989 Nov 10;246(4931):815–818. doi: 10.1126/science.2573153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto C. Quantal analysis of excitatory postsynaptic potentials induced in hippocampal neurons by activation of granule cells. Exp Brain Res. 1982;46(2):170–176. doi: 10.1007/BF00237173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



