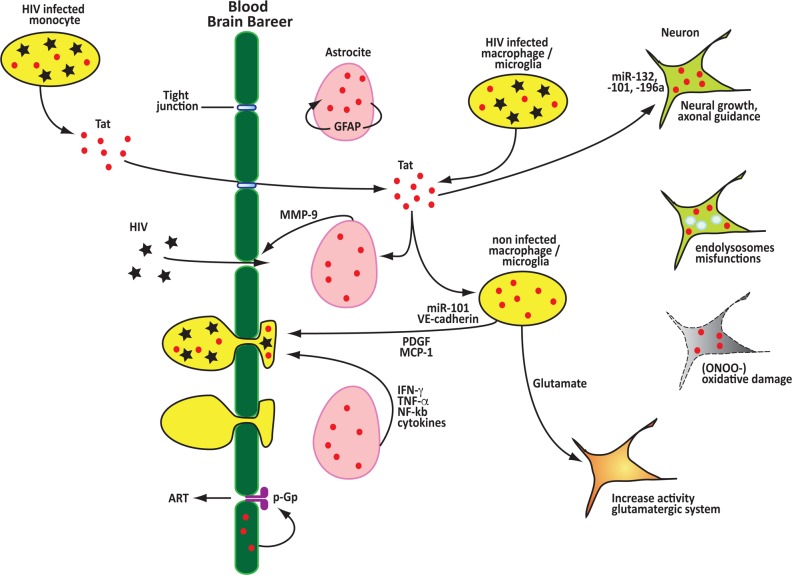
Figure 3. Tat contributes to the disruption of the blood brain barrier, neuroinflammation and neurotoxicity.
Extracellular Tat can passively cross the BBB decreasing the expression of tight junctions proteins and inducing the expression of factors that promote the disruption of the BBB. After crossing the BBB Tat is efficiently taken up by multiple cells, including neurons and astrocytes, this results in the release of several soluble factors that promote neuroinflammation and function as monocyte chemoattractant facilitating the invasion of the CNS by infected monocytes and macrophages. Tat directly induces neuronal toxicity by modulating the expression of miRNAs, disrupting endolysosomes functions, promoting oxidative damage and inpairing the functions of the glutamatergic neurotransmission system. Tat can also promote the remaval of anti retro viral drugs from the CNS by upregulating the P-glycoprotein (P-gp) pump.