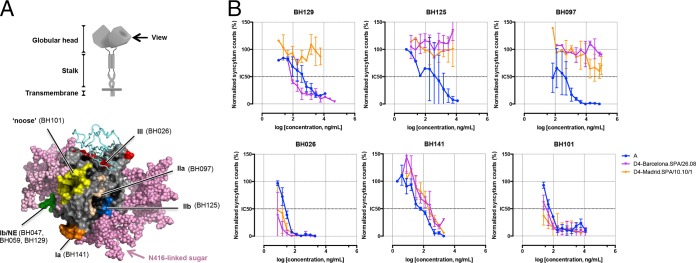
FIG 1.
Neutralization activity of a panel of anti-MeV-H MAbs against 2 genotype D4 viruses. (A, top) Diagram of the MeV-H homodimeric structure. (Bottom) Radiographic crystallographic structure of the MeV-H globular head showing the location of the 6 antigenic sites. Antigenic sites are color-coded (orange, Ia; green, Ib or NE; wheat, IIa; blue, IIb; red, III; yellow, noose), indicating a representative antibody target. The signaling lymphocytic activation molecule immunoglobulin V domain and modeled N-linked sugars are shown as cyan ribbons and pink spheres, respectively. A side view is shown, as indicated at the top. The N416-linked sugar present in genotype D4 is highlighted. (B) Virus neutralization assay. Recombinant measles virus expressing 2 different MeV-H genotype D4 sequences or genotype A (vaccine strain) was incubated in the absence or presence of the indicated neutralizing antibody for 1 h at 37°C. Two days later, the numbers of enhanced green fluorescent protein-expressing foci in the presence and absence of MAbs were counted and compared. Neutralization is plotted as a percentage of the control for residual infection (y axis) by MAb concentration (x axis). For a given MAb-virus pair, the data represent the geometric means of results from at least 2 independent experiments performed in quadruplicate. NE, neutralizing epitope.