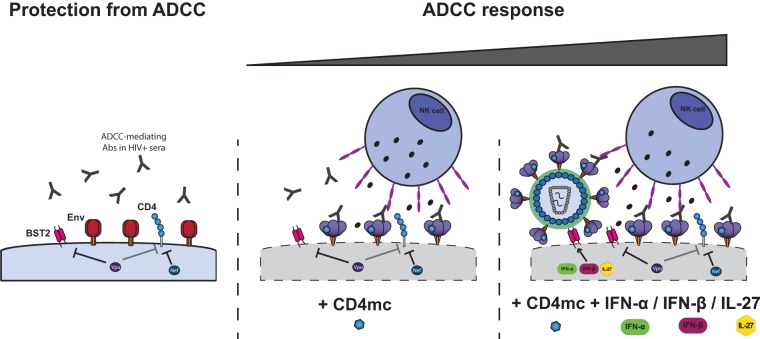
FIG 7.
Env conformation and its accumulation at the cell surface dictates sensitivity of HIV-1-infected cells to ADCC. ADCC-mediating Abs present in sera from HIV-1-infected individuals preferentially recognize Env in its CD4-bound conformation (1). To limit the exposure of this conformation, HIV-1 has evolved sophisticated mechanisms to counteract the host restriction factor BST-2 with the viral Vpu protein (7–9) and to downregulate CD4 by Nef and Vpu (7). Nef and Vpu decrease the accumulation of Env and its interaction with CD4 at the cell surface, two factors that determine the susceptibility of HIV-1-infected cells to ADCC. Small CD4 mimetics sensitize HIV-1-infected cells to ADCC mediated by HIV+ sera by forcing Env to sample its CD4-bound conformation (5). Type I IFN or IL-27 treatment, through upregulation of BST-2 despite Vpu activity, boosts the ability of CD4mc by increasing the amounts of CD4mc-sensitized Env available on the cell surface.