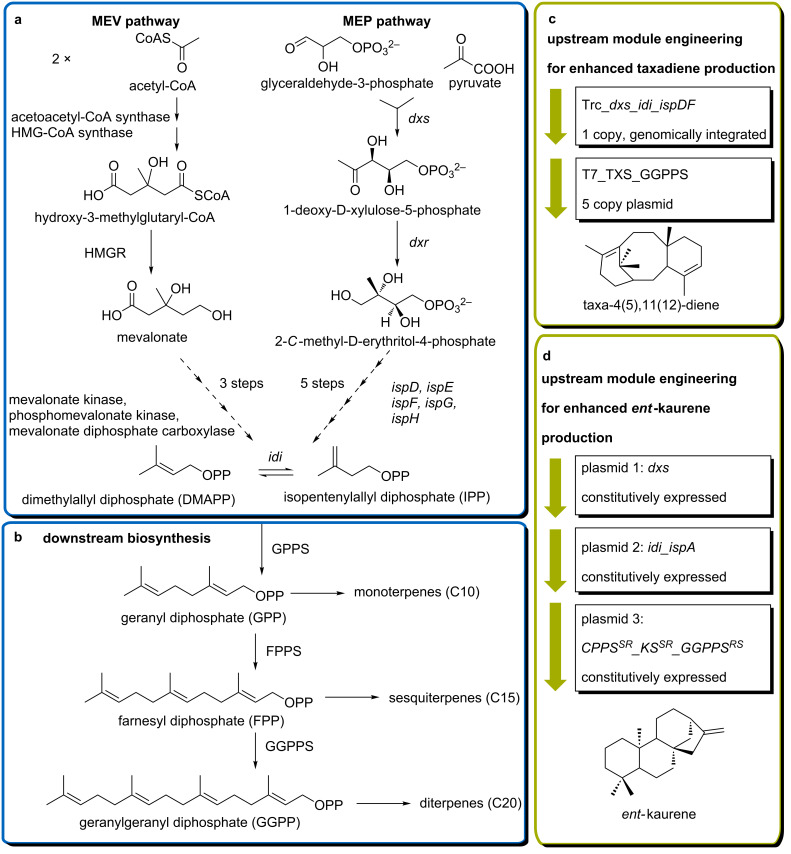
Scheme 1.
Isoprenoid biosynthetic pathways and examples for their engineering in heterologous production systems. a) Formation of central isoprenoid metabolites isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP) occurs via two distinct natural pathways. Designations MEV and MEP derive from significant intermediates: MEV = mevalonate-dependent and MEP= methylerythritol phosphate-dependent. b) Subsequent condensation of IPP and DMAPP by isoprenyl diphosphate synthases provides specific terpene synthases with their linear substrates. Terpenes are classified according to the carbon atom number in their basic scaffold, beginning with hemiterpenes (C5) and continuing in multiples of five. c) A possible strategy for MEP-pathway optimization for the improved production of the diterpene taxadiene reported by Ajikumar et al. [28]; targeted elements of the biosynthetic pathways and their expression manipulations are given. d) Selection of overexpression targets for the production of ent-kaurene reported by Kong et al. [29]; HMGR = hydroxymethylglutaryl(HMG)-CoA-reductase; dxs = 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase; dxr = 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase; ispD = 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol(ME)-4-phosphate cytidylyltransferase; ispE = 4-(cyt-5’-diphospho)-ME kinase; ispF = ME-2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase; ispG = hydroxylmethylbutenyl(HMB)-4-diphosphate synthase; ispH = HMB-4-diphosphate reductase; ispA = farnesyl diphosphate synthase from Escherichia coli; idi = IPP isomerase; GPPS = geranyl diphosphate synthase; FPPS = farnesyl diphosphate synthase, GGPPS = geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase; GGPPSRS = GGPPS from Rhodobacter sphaeroides; KSSR = ent-kaurene synthase from Stevia rebaudiana, CPPSSR = ent-copalyl diphosphate synthase from Stevia rebaudiana, Trc = Trc promoter; T7 = T7 promoter.