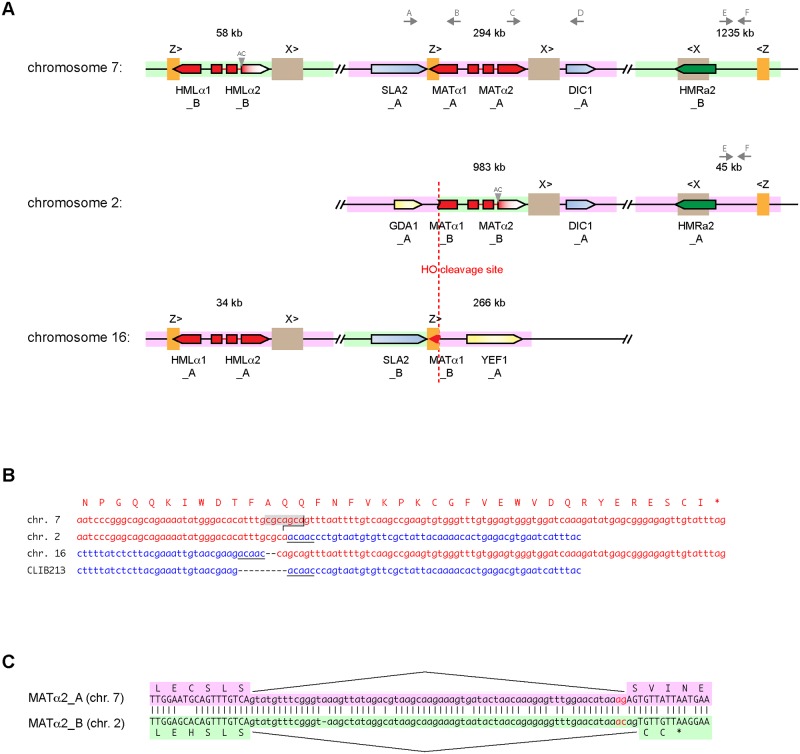
Fig 5.
(A) Organization of MAT, HML, and HMR loci in Z. parabailii ATCC60483. The genome contains 6 MAT-related regions, with 1 MAT, 1 HML, and 1 HMR locus derived from each of the A and B parents. Pink and green backgrounds indicate sequences from the A- and B-subgenomes, respectively. The MAT locus in the A-subgenome (position 294 kb on chromosome 7) is intact and expressed. The MAT locus of the B-subgenome has been broken into 2 parts by cleavage by HO endonuclease. All 6 copies of the X repeat region (654 bp) are identical in sequence, as are all 6 copies of the Z repeat region (266 bp). Gray triangles indicate the disruption of the splicing of intron 2 in MATα2 and HMLα2 of the B-subgenome. The binding sites for primers A–F used for PCR amplification are indicated by gray arrows. (B) Sequences at the MAT locus breakpoint. Red, MATα1-derived sequences. The HO cleavage site (CGCAGCA, giving a 4-nucleotide 3′ overhang) is highlighted in gray. Blue, the GDA1-YEF1 intergenic region from the equivalent region of Z. bailii CLIB213T and homologous sequences from the A-subgenome on Z. parabailii chromosomes (chrs.) 2 and 16. A 5-bp sequence (ACAAC) that became duplicated during the rearrangement is underlined. (C) Sequences of MATα2 intron 2 (lowercase) from the A- and B-subgenomes. An AG-to-AC mutation (red) at the 3′ end of the intron moved the splice site by 2 bp in the B-subgenome, causing a frameshift and premature translation termination. The splice sites in both genes were identified from RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) data.