Figure 4. Bacterial growth inhibition of E. faecalis with urine fractions from control patients compared to the same fractions of burned patients at 1 hour and 40 hours post-admission.
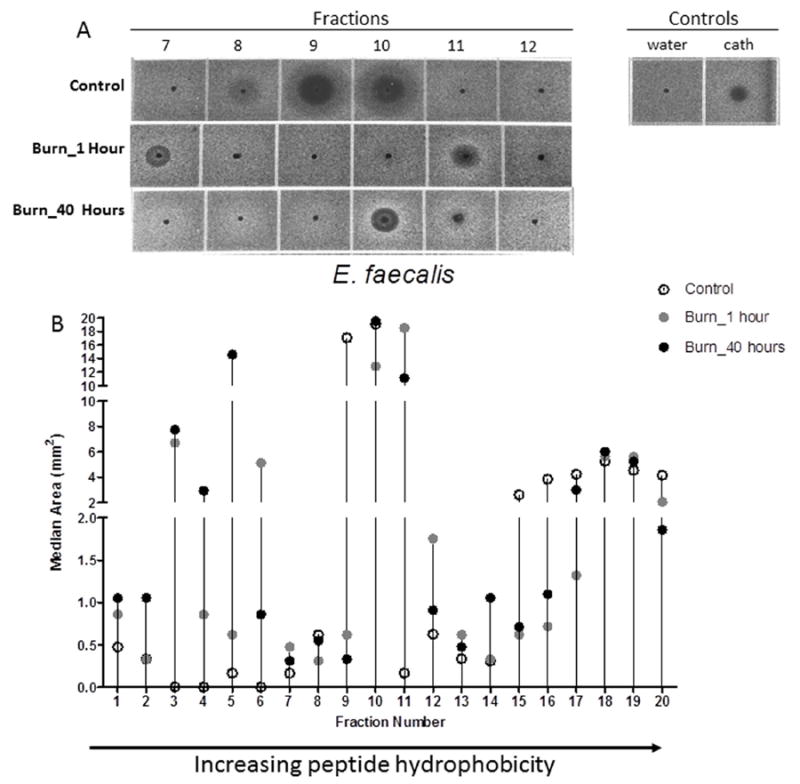
A) Zones of bacterial growth inhibition of E. faecalis present in fractions 7-12 withcontrol urine and fractions from burn patients 1 and 40 hours post-admission. B) Antimicrobial activity against E. faecalis is altered following burn injury in the majority of urine fractions and antimicrobial activity against E. faecalis demonstrates notable changes in multiple fractions. Arrow to the right indicates increasing peptide hydrophobicity. The median is shown for all groups: open circles: controls; grey circles: burn at 1 hour post-admission; black circles: burn at 40 hours post-admission. Fractions were assessed in duplicate with wells containing 1μl of sterile water and 1 μl LL-37 (100 μM; GeneScript) as negative and positive controls, respectively.
