Table 1.
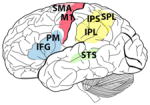
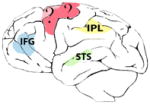
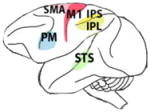
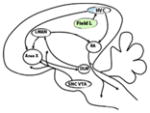
The brains of human, chimpanzee, macaque, marmoset and songbirds with the cerebral locations where mirror neurons have been investigated and found. On the brain images these are highlighted in red (motor areas), yellow (parietal areas), blue (premotor areas) and green (sensorial areas). For each species, the techniques used to record mirror neuron activity are specified. fMRI, functional magnetic resonance; EEG, electroencephalography; TMS, transcranial magnetic stimulation; PET, positron emission tomography; MEG, magnetoencephalography.
|
|
|

|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Homo sapiens (human) |
Pan troglotydes (chimpanzee) |
M. nemestrina M. mulatta M. fascicularia M. fuscata (macaque) |
Callitris jaccus (marmoset) |
Melospiza georgiana (swamp sparrow) Lonchura striata domestica (Bengalese finch) |
| fMRI PET TMS MEG EEG single-cell |
PET | fMRI EEG single-cell |
single-cell | single-cell |
| Supplementary motor area (SMA), primary motor cortex (M1), superior temporal sulcus (STS), inferior frontal gyrus (IFG), inferior parietal lobule (IPL), premotor cortex (PM), intraparietal sulcus (IPS), superior parietal lobule (SPL) | Inferior parietal lobule (IPL), superior temporal sulcus (STS), inferior frontal gyrus (IFG) | Supplementary motor area (SMA), primary motor cortex (M1), inferior parietal lobule (IPL), intraparietal sulcus (IPS), premotor cortex (PM), | Premotor cortex (PM), superior temporal sulcus (STS), | High vocal center (HVC) Field L |
