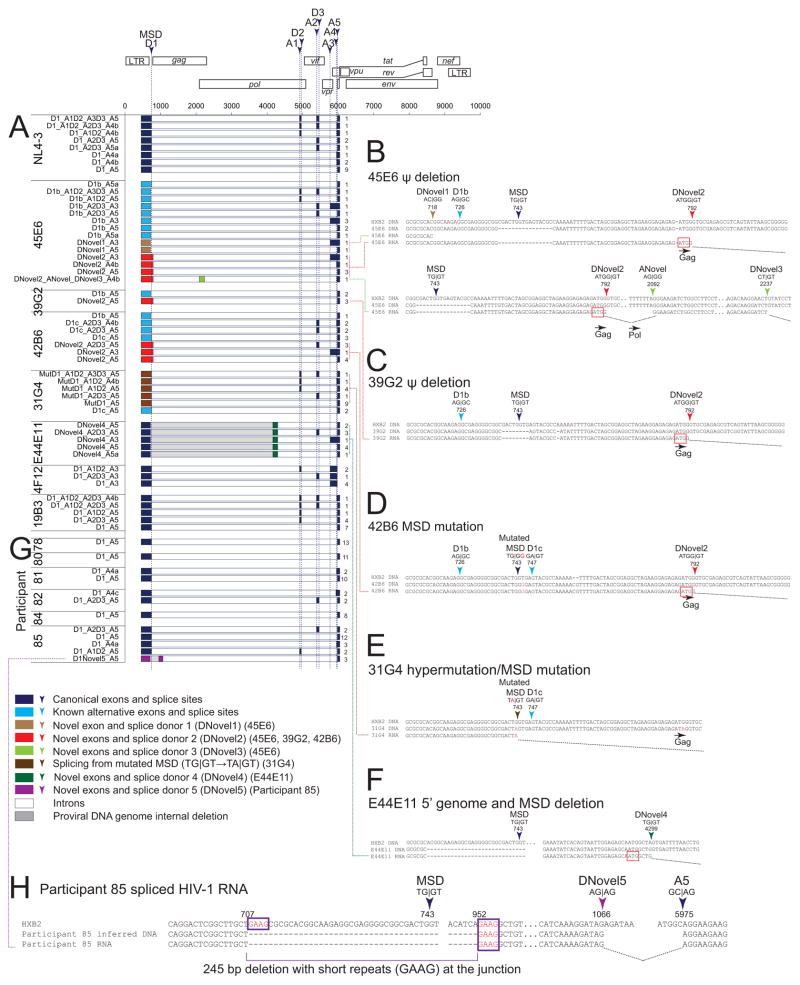
Figure 2. HIV-1 proviruses can bypass MSD defects by activating novel SDSs and splicing into canonical SASs in vitro and ex vivo.
(A) Spliced HIV-1 RNA transcripts from reconstructed patient-derived proviruses. Numbers on the right indicate the number of isolates from cloning of PCR products. (B–F) Sequences of canonical (Ocwieja et al., 2012; Schwartz et al., 1990a), known alternative (Ocwieja et al., 2012), and novel splice sites. (G) Spliced HIV-1 RNA from patient resting CD4+ T cells upon ex vivo activation. (H) Sequences of novel splice sites in participant 85. Purple box, short sequence repeats likely related to the 245 bp deletion encompassing MSD. See also Table S1–S5, Figures S2–S6.