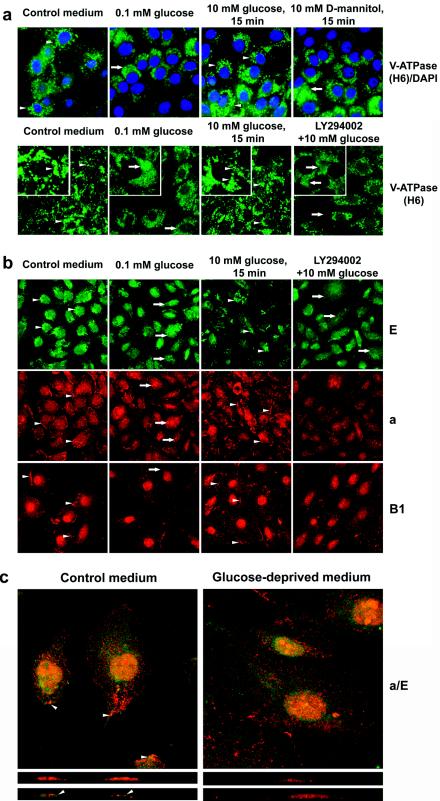
FIG. 4.
Glucose-dependent, LY294002-sensitive translocation of V-ATPase in renal epithelial cells. (a) LLC-PK1 cells were grown on coverslips in standard conditions. Prior to the experiments, cells were incubated in glucose-free DMEM overnight and were then stimulated with 10 mM glucose or 10 mM d-mannitol (upper panels) for 15 min. If the effect of PI3K inhibition was studied, LY294002 (25 μM) and vehicle were added 30 min prior to glucose addition. Then cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained with H6.1 V-ATPase antibody. Nuclei were (upper panels) or were not (lower panels) counterstained with DAPI. In the presence of glucose (before glucose deprivation and after glucose replacement) bright vesicular staining of V-ATPase is visible in the majority of cells (see arrowheads, for example). Glucose deprivation induced appearance of diffuse staining (see insets, arrows, for example). (b) HK-2 cells were grown on coverslips in standard conditions. Prior to the experiments, cells were incubated in glucose-free DMEM overnight and were then stimulated with glucose with or without LY294002, as described above. Then cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained with antibodies to V1 subunits E and B1 and Vo subunit a. Vesicular staining of subunit E and peripheral perimembrane staining of B1 and a subunits in control conditions or after stimulation with glucose is seen (see arrowheads, for example). Glucose-deprived or LY294002-treated cells show more diffuse staining for the E subunit, disappearance of membrane staining for subunits a and B1, and translocation of subunit a to large vesicles (see arrow, for example). (c) Colocalization of a and E subunits in perimembrane and apical areas is observed only in the presence of glucose (arrowheads). Confocal images of optical 0.5-μM sections (upper panels) and vertical (XZ) sections (lower panels) are shown.