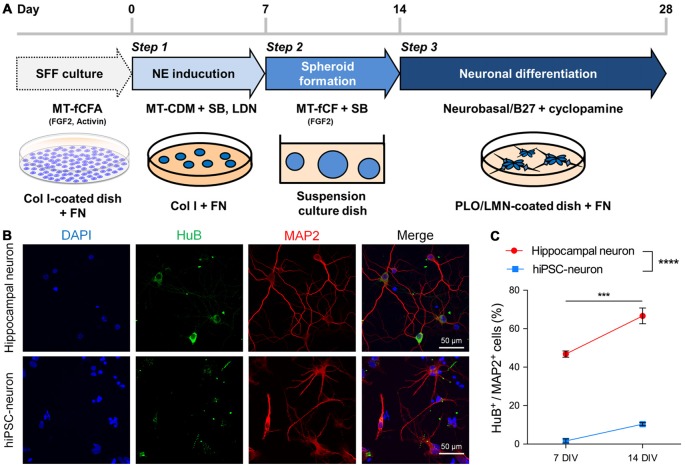
Figure 1.
Human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSC-neurons) on a glass dish barely expressed hippocampal neuronal markers. (A) Schematic method for neuronal differentiation. The protocol consists of three steps: Step 1, NE induction (days 0–7) by dual-smad inhibition with SB and LDN; Step 2, spheroid formation (days 7–14) on suspension culture dishes in the presence of FGF2 and SB; Step 3, neuronal differentiation (days 14–28), by dissociating cells and plating them back on PLO/LMN-coated dishes in the presence of cyclopamine. SFF, single-cell and feeder-free; NE, neuroectoderm; SB, SB431542 (TGFβ inhibitor); LDN, LDN193189 (BMP inhibitor); Col I, collagen type I; FN, fibronectin; PLO, poly-L-ornithine; LMN, laminin. (B) Representative images of cultured hippocampal neurons (top) and hiPSC-neurons (bottom) at 14 days in vitro (DIV), immunostained with the hippocampal CA3 pyramidal cell marker HuB and the mature dendritic marker microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2). (C) The percentage of HuB+ cells/MAP2+ cells was 46.8 ± 1.44% at 7 DIV and 66.6 ± 3.64% at 14 DIV in hippocampal neurons and was 1.61 ± 0.91% at 7 DIV and 10.4 ± 0.71% at 14 DIV in hiPSC-neurons. Data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). ***P < 0.001; hippocampal neuron 7 DIV vs. 14 DIV, **** P < 0.0001; hippocampal neuron vs. hiPSC-neurons both at 7 and 14 DIV, Tukey’s test after ANOVA, N = 5 samples for hippocampal neuron, four samples for hiPSC-neurons (each sample includes 42–114 cells).